In a table, data is arranged into columns. Each column stores one data element, such as a first name, one line of an address, a price, or any similar discrete unit of information.
When columns are created in a table, they are given a name that identifies their purpose, such as FirstName or Address1. In most databases, you must also specify additional properties, such as how long the longest entry in the column will be, and what type of data the column will contain - characters, integers, floating-point numbers, dates or times, and so on. Other column properties can include whether the column is the table's primary key, whether users must enter a value into it, and what its default value is.
Each column in a table has a set of properties. Each property defines one characteristic, such as the name, data type or length, of a column. The entire set of properties for a column makes up that column’s definition in your database table.
You can set column properties directly in your database table in a database diagram. Three column properties are required
When you view your table in column properties view, the column properties are laid out in a grid. In this grid, you can choose which properties you want to see. You can hide the properties that you rarely define and show the properties that you define more frequently. You can also resize the columns in the grid so that the properties are easy to read.
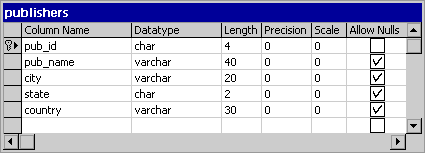
 Column properties
Column properties