- Open a form or report in Design view.
- Click the Text Box tool
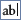 in the toolbox.
in the toolbox. - In the detail section, click where you want to place the text box.
- Do one of the following:
Place the insertion point in the text box and type an expression that calculates a total.
Select the text box, click Properties
 on the toolbar, and type the expression in the ControlSource property box. In a Microsoft Access database (.mdb), to use the Expression Builder to create the expression, click the Bu
on the toolbar, and type the expression in the ControlSource property box. In a Microsoft Access database (.mdb), to use the Expression Builder to create the expression, click the Bu ild button next to the ControlSource property box.
ild button next to the ControlSource property box.
Notes
- If you need more room to type an expression in the ControlSource property box, press SHIFT+F2 to open the Zoom box.
- If a form or report is based on a query, you may want to put the expression in the query instead of in a calculated control. It may improve performance, and if you are going to calculate totals for groups of records, it's easier to use the name of a calculated field in an aggregate function.
If you want to do complex calculations using spreadsheet functions, use the Microsoft Office Spreadsheet Component. For all other calculations, you can use the bound span control.
 Using the Spreadsheet Component
Using the Spreadsheet Component
- Open the data access page in Design view.
- If they aren't already on the page, add the controls that will contain the data you want to use in the calculation.
- Click the Office Spreadsheet tool
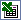 in the toolbox, and then click where you want the upper-left corner of the spreadsheet to be on the data access page.
in the toolbox, and then click where you want the upper-left corner of the spreadsheet to be on the data access page. - In any cell in the spreadsheet, enter a formula that uses the HTML Host function to refer to the fields used in the calculation, and the specific operation you want to perform on the field's values expressed as a combination of operators, identifiers, and values.
Example To multiply the value in the Quantity field by the value in the UnitPrice field, type:
=Host().Quantity.value*Host().UnitPrice.value
Example To multiply the value in the UnitPrice field by a percentage rate stored in cell C1, type:
=$C$1*Host().UnitPrice.value
Notes
- To see the name of a spreadsheet, select the control, and then click Properties
 on the toolbar. The property sheet title bar displays the spreadsheet name.
on the toolbar. The property sheet title bar displays the spreadsheet name. - You can use spreadsheet functions, which, in Microsoft Access, are available only in this control.
- Most likely, you'll want the calculated value to display in an area that looks like the other controls on the data access page. To do this you can modify the appearance of the spreadsheet so it looks like a text box.
- Open the data access page in Design view.
- If the expression will reference field names, the fields must be in the page's data definition. Either add the fields to the page as bound span controls, or add the fields as bound text boxes.
The page will load faster in Page view and in Microsoft Internet Explorer if you use bound span controls.
-
Create another control by clicking the Bound Span tool
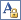 or the Text Box tool
or the Text Box tool  in the toolbox, and then click where you want the upper-left corner of the control to be on the page.
in the toolbox, and then click where you want the upper-left corner of the control to be on the page. - To display the property sheet, make sure that the control is selected, and then click Properties
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar. - In the ControlSource property box, type an alias and an appropriate expression. To reference fields on the page, use the names of the fields in the expression. For example, if you want to compute the extended price for a record in the Order Details table, type:
ExtendedPrice: UnitPrice*Quantity
If you don't specify an alias, you must type an equal sign (=) before the expression. Microsoft Access will automatically supply an alias
— for example, Expr1.