About the Table Analyzer's query (MDB)
Note The information in this topic applies only to a Microsoft Access database (.mdb).
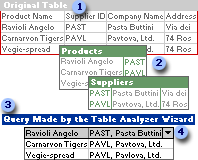
 Original table
Original table
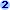 Tables created by the Table Analyzer
Tables created by the Table Analyzer
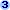 Query created by the Table Analyzer
Query created by the Table Analyzer
 Lookup list
Lookup list
If your Microsoft Access database has a table that contains repeating information in one or more fields, you can use the Table Analyzer to split the data into related tables so that you can store data more efficiently. This process is called normalization.
The Table Analyzer divides one table that contains repeating information into separate tables in which each type of information is stored only once. This makes the database more efficient and easier to update, and reduces its size. After the wizard divides the data, you can still view and work with the data in one place by having the wizard create a query.
You can use the query to update data from more than one table at the same time. The query also offers other timesaving features to increase the accuracy of your data.
- If you change a field that is repeated in the query, all records with that value are automatically updated because you are actually updating just one field in the query's underlying table.
- From the new tables, the query inherits Lookup fields, which let you change field values by picking values from a list instead of having to correctly type a value. The Lookup list looks up values from the underlying table. When the same value applies to more than one record, you can ensure accuracy and consistency by picking that value from the list each time.
- Forms, reports, and data access pages that were previously based on the original table will automatically be based on the query now, because the wizard assigns the original table's name to the query and renames the table.
- Existing forms and reports based on the query will inherit automatic field updates. New forms and reports will also inherit Lookup lists.
