Calculates variance based on the entire population.
Syntax
VARP(number1,number2,...)
Number1, number2, ... are 1 to 30 number arguments corresponding to a population.
Remarks
- VARP assumes that its arguments are the entire population. If your data represents a sample of the population, then compute the variance using VAR.
- The equation for VARP is:
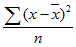
where x is the sample mean AVERAGE(number1,number2,…) and n is the sample size.
- Logical values such as TRUE and FALSE and text are ignored. If logical values and text must not be ignored, use the VARPA worksheet function.
Example
Suppose all 10 tools stamped from the same machine during a production run are collected and measured for breaking strength.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
- Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
- Select the example in the Help topic. Do not select the row or column headers.
Selecting an example from Help
- Press CTRL+C.
- In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
- To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Tools menu, point to Formula Auditing, and then click Formula Auditing Mode.
|
|
 How?
How?