Returns the kurtosis of a data set. Kurtosis characterizes the relative peakedness or flatness of a distribution compared with the normal distribution. Positive kurtosis indicates a relatively peaked distribution. Negative kurtosis indicates a relatively flat distribution.
Syntax
KURT(number1,number2,...)
Number1, number2, ... are 1 to 30 arguments for which you want to calculate kurtosis. You can also use a single array or a reference to an array instead of arguments separated by commas.
Remarks
- The arguments must be either numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
- If an array or reference argument contains text, logical values, or empty cells, those values are ignored; however, cells with the value zero are included.
- If there are fewer than four data points, or if the standard deviation of the sample equals zero, KURT returns the #DIV/0! error value.
- Kurtosis is defined as:
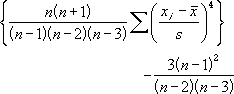
where:
s is the sample standard deviation.
Example
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
- Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
- Select the example in the Help topic. Do not select the row or column headers.
Selecting an example from Help
- Press CTRL+C.
- In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
- To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Tools menu, point to Formula Auditing, and then click Formula Auditing Mode.
|
|
 How?
How?