Returns covariance, the average of the products of deviations for each data point pair. Use covariance to determine the relationship between two data sets. For example, you can examine whether greater income accompanies greater levels of education.
Syntax
COVAR(array1,array2)
Array1 is the first cell range of integers.
Array2 is the second cell range of integers.
Remarks
- The arguments must either be numbers or be names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
- If an array or reference argument contains text, logical values, or empty cells, those values are ignored; however, cells with the value zero are included.
- If array1 and array2 have different numbers of data points, COVAR returns the #N/A error value.
- If either array1 or array2 is empty, COVAR returns the #DIV/0! error value.
- The covariance is:
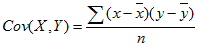
where x and y are the sample means AVERAGE(array1) and AVERAGE(array2), and n is the sample size.
Example
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
- Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
- Select the example in the Help topic. Do not select the row or column headers.
Selecting an example from Help
- Press CTRL+C.
- In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
- To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Tools menu, point to Formula Auditing, and then click Formula Auditing Mode.
|
|
 How?
How?