Multiple Peak Calibration for Spectrometer to Angstroms Calculations
When Probe for EPMA calculates the calibrated angstrom of a given spectrometer position, by default the program bases the conversion on the constant offset calculated at the element peak position for each analytical channel using the following standard expression:
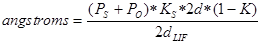
where: 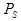 = the position for the spectrometer
= the position for the spectrometer
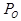 = the measured or calibrated
spectrometer offset from the theoretical (constant or variable)
= the measured or calibrated
spectrometer offset from the theoretical (constant or variable)
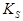 = the conversion factor for
spectrometer units to LIF angstroms (SCALERS.DAT)
= the conversion factor for
spectrometer units to LIF angstroms (SCALERS.DAT)
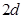 = the 2d spacing of the spectrometer
crystal
= the 2d spacing of the spectrometer
crystal
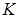 = the crystal constant
(CRYSTALS.DAT)
= the crystal constant
(CRYSTALS.DAT)
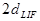 = the 2d for LIF (4.0267)
= the 2d for LIF (4.0267)
To calculate a variable spectrometer offset, the program utilizes a series of peak center calibrations performed in the StartWin application as described above. The multiple peak calibration data is stored in the .CAL files described above and the following is a small part of such a file produced by running a series of peak calibrations on an SX-51 microprobe where the spectrometer positions range roughly from 22000 to 86000.
2 "PET" 5
"si" "ka" 81454.48 81426 14
"s" "ka" 61415.59 61354 327
"k" "ka" 42776.79 42730 374
"ti" "ka" 31430.02 31403 22
"cr" "ka" 26186.62 26175 24
2 -107.9718 5.904327E-03 -5.182411E-08
The above calibrations are for the PET crystal on spectrometer two using K line intensities. The calibration is based on 5 peak centers using Si, S, K Ti and Cr. These elements are designed to cover the full range of the spectrometer crystal whenever practical. The first column of numbers are the theoretical calculated peak positions and the second column of numbers are the actual or measured peak positions. The offset between these two sets of spectrometer positions is fit to a 2nd order polynomial and the coefficients are stored on the last line of the data set as can be seen above. The actual application of the variable offset for the purposes of spectrometer position to angstrom conversion is as follows:
First, the program calculates the expected peak position for the calibration element used for the wavescan based on the variable offset obtained from the calibration coefficients measured above using the polynomial expression:
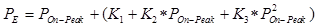
where: 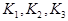 = the calibration coefficients from the
multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
= the calibration coefficients from the
multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
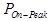 = the theoretical on peak position of
the calibration element
= the theoretical on peak position of
the calibration element
This expected on-peak position from the multiple peak calibration coefficients is used to calculate the difference from the actual measured on-peak position as follows:
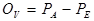
where: 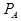 = the actual or measured on-peak
spectrometer position
= the actual or measured on-peak
spectrometer position
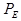 = the expected spectrometer position
based on the previous calculation
= the expected spectrometer position
based on the previous calculation
This spectrometer position offset is used to temporarily modify the variable offset calibration intercept coefficient (first term) obtained from the .CAL file as follows:
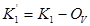
where: 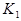 = the intercept coefficient from the
multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
= the intercept coefficient from the
multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
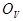 = the difference between the actual
on-peak and the expected on-peak from the previous equation
= the difference between the actual
on-peak and the expected on-peak from the previous equation
In this way, the modified expected position calculation will obtain a modified variable offset equal to the constant offset when the spectrometer position is at the actual on-peak position, but the calculated offset will still vary based on the slope and curvature terms as the spectrometer position departs from the on-peak position as follows:
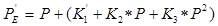
where: 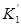 = the modified intercept term of the
multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
= the modified intercept term of the
multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
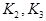 = the slope and curvature coefficients
of the multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
= the slope and curvature coefficients
of the multiple peak calibration polynomial fit
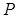 = the spectrometer position
= the spectrometer position
By doing this, the angstrom calculation is based on the multiple peak calibration for high accuracy over the entire spectrometer range, but can still be re-calibrated simply by a single re-peaking of the spectrometer peak position in the future.