Channel-to-Channel Skew
For dynamic generation, channel-to-channel skew is defined as the time difference between corresponding edges on the data channels. For example, if two data channels are each programmed to transition from low to high level on a particular sample, the time difference between the rising edges on the two channels would be the channel-to-channel skew between the two channels.
For dynamic acquisition, channel-to-channel skew is defined as the difference between the sampling times for each data channel. When each sample is acquired, the point in time at which each data channel is sampled with respect to every other data channel is not identical, but the difference is within some small window of time. This time window is referred to as the channel-to-channel skew.
The following figure shows the channel-to-channel skew of a group of signals.
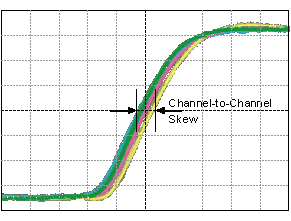
Specified channel-to-channel skew generally refers to the skew across all data channels on a device.