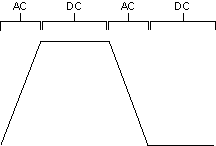
AC and DC Current
AC current is current sourced/sunk during the transition between low and high level states driving a capacitive load (such as a cable) or an inductive load (such as a device interconnect). DC current is the current sourced/sunk when the generation terminals are at a static voltage driving a resistive load. The illustration below of a digital waveform shows when AC or DC current is sourced/sunk.
Use the following formulas to calculate AC current.
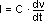
where
I is current in amps,
C is load capacitance in farads,
and
dV/dt is the rate of change of the voltage level in volts/s,
or
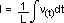
where
I is the current in amps,
L is the inductive loading in henrys,
and
V(t) is the voltage in volts as a function of time.
Use the following formula to calculate DC current.
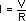
where
I is current in amps,
V is voltage level in volts,
and
R is resistance in ohms.