AC Waveform Characteristics
The following terms describe some of the common AC waveform characteristics.
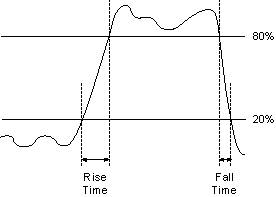
- Rise time and fall time—Rise time (trise) is
the time that it takes a signal to rise from 20% to 80% of the voltage between the voltage low level and the voltage high level. Fall time (tfall)is the time that it takes a signal to fall from 80% to
20% of the voltage between the voltage low level and the voltage high level.
The following figure illustrates rise and fall time.
- Preshoot and Overshoot—Preshoot and overshoot are peak distortions preceding (preshoot) or following
(overshoot) an edge. The following figure shows an example of preshoot
and overshoot on a signal.
Note Together, overshoot, preshoot, and undershoot are called aberrations. 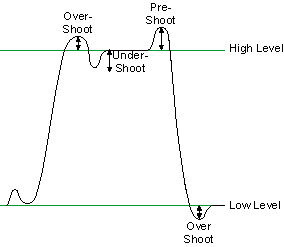
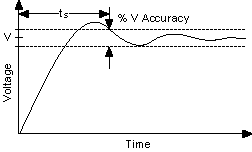
- Settling time—Settling time (tS) is the time required for an
amplifier, relay, or other circuits to reach a stable mode of operation.
In the context of signal acquisition, the settling time for a full-scale step is
the amount of time required for a signal to reach a certain accuracy and stay
within that accuracy range.
The following figure illustrates settling time on a digital signal.
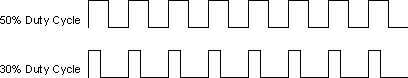
- Duty cycle—For clock signals, the percentage of the waveform period that the waveform is at logic high level.
The following figure shows the difference between two waveforms with different duty cycles. Notice that the 30% duty-cycle waveform is at logic high level for less time than the 50% duty cycle waveform.