IMAQ Divide VI
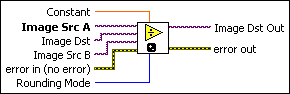
Owning Palette: OperatorsInstalled With: NI Vision Development ModuleDivides one image by another image or an image by a constant.




 |
Constant is the value that divides Image Src A for image-constant operations. |
||||||
 |
Image Src A is a reference to the first source image. |
||||||
 |
Image Dst is the reference to the destination image. If connected, Image Dst is converted to an RGB image. If not connected, Image Src is converted to an RGB image. |
||||||
 |
Image Src B is the reference to the second source image. |
||||||
 |
error in (no error) describes the error status before this VI or function runs. The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
|
||||||
 |
Rounding Mode specifies the type of rounding to use when dividing image pixels. The following options are available.
|
||||||
 |
Image Dst Out is the reference to the destination (output) image that receives the processing results of the VI. If the Image Dst is connected, Image Dst Out is the same as Image Dst. Otherwise, Image Dst Out refers to the image referenced by Image Src A. |
||||||
 |
error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces. Right-click the error out indicator on the front panel and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Details
The image type of Image Src B depends on the image type of Image Src A.
- If Image Src A is a signed 16-bit image, Image Src B must be a signed 16-bit image or an unsigned 8-bit image.
- If Image Src A is a 32-bit floating-point image, Image Src B must be a 32-bit floating-point image, signed 16-bit image, or unsigned 8-bit image.
- If Image Src A is a complex image, Image Src B must be a complex image, 32-bit floating-point image, signed 16-bit image, or unsigned 8-bit image.
- If Image Src A is a 32-bit RGB image, Image Src B must be a 32-bit RGB image, complex image, 32-bit floating-point image, signed 16-bit image, or unsigned 8-bit image.
Otherwise, Image Src B must be the same type as Image Src A.
When the value of a pixel in Image Src B is 0, the result of the divide operation for the pixel is either the maximum or minimum pixel value for the image type. If the corresponding pixel value in Image Src A is greater than 0, then the result is the maximum possible pixel value for the image type. Otherwise, the result is the minimum possible value for the image type.