IMAQ Convolute VI
Owning Palette: FiltersInstalled With: NI Vision Development ModuleFilters an image using a linear filter. The calculations are performed with either integers or floating points, depending on the image type and the contents of the kernel.
 |
Note This VI modifies the source image. If you need the original source image, create a copy of the image using the IMAQ Copy before using this VI. |


 |
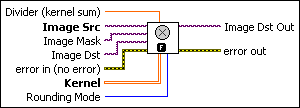
Divider (kernel sum) is a normalization factor that can be applied to the sum of the obtained products. Under normal conditions the divider should not be connected. If connected and not equal to 0, the elements internal to the matrix are summed and then divided by this normalization factor. |
||||||
 |
Image Src is a reference to the source image. |
||||||
 |
Image Mask is an 8-bit image that specifies the region of the small image that will be copied. Only those pixels in the Image Src (Small) image that correspond to an equivalent non-zero pixel in the mask image are copied. All other pixels keep their original values. The entire image is processed if Image Mask is not connected. |
||||||
 |
Image Dst is a reference to the destination image. |
||||||
 |
error in (no error) describes the error status before this VI or function runs. The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
|
||||||
 |
Kernel is a 2D array that contains the convolution matrix to apply to the image. The size of the convolution is fixed by the size of this array. The array can be generated by standard LabVIEW programming techniques or the IMAQ GetKernel VI or the IMAQ BuildKernel VI. If the kernel contains fewer than three rows or three columns, no convolution is performed. |
||||||
 |
Rounding Mode specifies the type of rounding to use when dividing image pixels. The following options are available.
|
||||||
 |
Image Dst Out is a reference to the destination image. If Image Dst is connected, Image Dst Out is the same as Image Dst. Otherwise, Image Dst Out refers to the image referenced by Image Src. |
||||||
 |
error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces. Right-click the error out indicator on the front panel and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Details
The connected source image must have been created with a border capable of supporting the size of the convolution matrix. A 3 × 3 matrix must have a minimum border of 1, a 5 × 5 matrix must have a minimum border of 2, and so on. The border size of the destination image is not important.
A convolution matrix must have odd-sized dimensions so that it contains a central pixel. If one of the Kernel dimensions is even, the function does not take into account the odd boundary, farthest out on the matrix. For example, if the input Kernel is 6 × 4 (X = 6 and Y = 4), the actual convolution is 5 × 3. Both the sixth line and the fourth line are ignored.
Calculations using an 8-bit or 16-bit Image Src input are made in integer mode provided that the kernel contains only integers. Calculations using a 32-bit floating-point Image Src input are made in floating-point mode.
The processing speed corresponds to the size of the kernel. A 3 × 3 convolution processes 9 pixels and a 5 × 5 convolution processes 25 pixels.
Examples
Refer to the following for an example that uses this VI.
- Examples\Vision\2. Functions\Binary Analysis\Particle Analysis Example.vi