 |
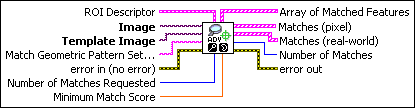
ROI Descriptor specifies the region of the inspection image in which to perform geometric matching. This region must be a single rectangle or rotated rectangle contour. By default, the VI uses the entire inspection image for matching.
 |
Global Rectangle contains the coordinates of the bounding rectangle.
|
 |
Contours are each of the individual shapes that define an ROI.
 |
ID refers to whether the contour is the external or internal edge of an ROI.
|
 |
Type is the shape type of the contour.
|
 |
Coordinates indicates the relative position of the contour.
|
|
|
 |
Image is a reference to the inspection image in which you want to search for the
template image
|
 |
Template Image is a reference to the template for which you want to search during the
matching phase. The template image is an output of the IMAQ Learn Geometric Pattern VI.
|
 |
Match Geometric Pattern Setup Data is a string that contains information from the IMAQ Setup Match Geometric Pattern VI or the IMAQ Advanced Setup Match Geometric Pattern VI. If this input is not connected, the VI uses default parameters for all unconfigured options.
|
 |
error in (no error) describes the error status before this VI or function runs. The default is
no error. If an error occurred before this VI or
function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to
error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error
occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs,
it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the
description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring
error out from one node to error in of the next node.
 |
status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred before this VI or function ran or FALSE
(checkmark) to indicate a warning or that no error occurred before this VI or function ran.
The default is FALSE.
|
 |
code is the error or warning code. If status is
TRUE, code is a nonzero error code. If status is FALSE, code is 0 or a warning code.
|
 |
source describes the origin of the error or warning and is, in most cases, the
name of the VI or function that produced the error or warning. The default is an empty
string.
|
|
 |
Number of Matches Requested is the number of valid matches expected.
|
 |
Minimum Match Score is the smallest score a match can have to be considered valid. The data range for a match is between 0 and 1000.
|
 |
Array of Matched Features is an array of a list of geometric features associated with each match
returned.
 |
Matched Features is a list of geometric features associated with a given match.
 |
Feature Type is the type of geometric feature.
|
 |
Feature Data is an array that describes the geometric feature. The elements of this array should be interpreted according to the feature type in the following manner:
| Circle |
- Element 0—X coordinate of the center of circle.
- Element 1—Y coordinate of the center of circle.
- Element 2—Radius of circle.
|
| Ellipse |
- Element 0—X coordinate of the center of ellipse.
- Element 1—Y coordinate of the center of ellipse.
- Element 2—Orientation in degrees of the major axis.
- Element 3—The length of the semi-major axis.
- Element 4—The length of the semi-minor axis.
|
| Constant Curve |
- Element 0—X coordinate of the center of the constant curve.
- Element 1—Y coordinate of the center of the constant curve.
- Element 2—The starting angle in degrees of the constant curve.
- Element 3—The ending angle in degrees of the constant curve.
- Element 4—The radius of the circle subtended by the constant curve.
|
| Rectangle/Leg |
- Element 0—X coordinate of the location of the center of the rectangle/leg.
- Element 1—Y coordinate of the location of the center of the rectangle/leg.
- Elements 2 and 3—The first corner point (x, y) of the rectangle/leg.
- Elements 4 and 5—The second corner point (x, y) of the rectangle/leg.
- Elements 6 and 7—The third corner point (x, y) of the rectangle/leg.
- Elements 8 and 9—The fourth corner point (x, y) of the rectangle/leg.
- Element 10—The orientation of the rectangle/leg in degrees with respect to the horizontal axis.
- Element 11—The width of the rectangle/leg.
- Element 12—The height of the rectangle/leg.
|
| Corner |
- Element 0—X coordinate of the corner position.
- Element 1—Y coordinate of the corner position.
- Element 2—The orientation of the corner.
- Element 3—The enclosed angle of the corner.
- Element 4—Specifies whether or not the corner is a virtual corner. A value of 0 means that the corner is not a virtual corner. A value of 1 means that the corner is a virtual corner.
|
| Parallel Line Pair |
- Elements 0 and 1 —The start point (x, y) of the first line.
- Elements 2 and 3—The end point (x, y) of the first line.
- Elements 4 and 5—The start point (x, y) of the second line.
- Elements 6 and 7—The end point (x, y) of the second line.
- Element 8—The orientation in degrees of the parallel line pair with respect to the horizontal axis.
- Element 9—The distance of the two lines from one another.
|
| Parallel Line Pairs |
- Elements 0–9—The first parallel line pair.
- Elements 10–19—The second parallel line pair.
- Element 20—The orientation in degrees of the pair of parallel line pairs with respect to the horizontal axis.
- Element 21—The distance the two parallel line pairs are from one another as measured by the midline of the first to the midline of the second.
|
| Line |
- Elements 0 and 1—The start point (x,y) of the line.
- Elements 2 and 3—The end point (x,y) of the line.
- Element 4—The length of the line.
- Element 5—The orientation in degrees of the line with respect to the horizontal axis.
|
| Closed Curve |
- Elements 0 and 1—The center point (x,y) of the closed curve.
- Element 2—The arc length of the closed curve element.
- Elements 3 and 4—The first of N contour points (x,y) of the closed curve.
- Elements 5 and 6—The second of N contour points (x,y) of the closed curve.
- Elements k and k+1—The (k–1)/2 contour point (x,y) of the closed curve.
- Elements 2*N+1 and 2*N+2—The last of N contour points (x,y) of the closed curve.
|
|
|
|
 |
Matches (pixel) contains information about a match found in the image.
 |
Position is a point-coordinate cluster corresponding to the location of the template
origin.
|
 |
Angle is the rotation angle, in degrees, of the template at the current match
location.
|
 |
Scale is the ratio of the size of the matched template relative to the original
template image, expressed as a percentage.
|
 |
Score ranks the match results on a scale of 0 to 1000, where 0 equals no match
and 1000 equals a perfect match.
|
 |
Bounding Box is an array of five points that define the boundary of the template.
|
 |
Contrast Reversed specifies whether the match is an inverse of the template image. This parameter is TRUE if the match is an inverse of the template image. For example, the match is a white object on a black background but the template image is a black object on a white background. This parameter is FALSE if the match is not the inverse of the template image.
|
 |
Occlusion % is the percentage of the match that is occluded.
|
 |
Template Target Curve Score specifies how closely the curves in the match region of the inspection, or
target, image match the curves in the template. Score values can range from 0 to 1000, where a score of 1000 indicates that all template curves have a corresponding curve in the match region of the inspection image.
|
 |
Target Template Curve Score specifies how closely the curves in the match region of the inspection, or target, image match the curves in the template. Score values can range from 0 to 1000, where a score of 1000 indicates that all curves in the match region of the inspection image have a corresponding curve in the template image.
|
 |
Correlation Score specifies the accuracy of the match obtained by comparing the template image to the match region using a correlation metric that compares the two regions as a function of their pixel values. A score of 1000 indicates a perfect match, and a score of 0 indicates no match.
|
|
 |
Matches (real-world) contains information about a match found in the image.
 |
Note
Matches (real-world) may differ from Matches (pixel) if Image is a calibrated image. If Image is a calibrated image, Position, Angle, and Bounding Box are returned in real-world units. |
 |
Position is a point-coordinate cluster corresponding to the location of the template
origin.
|
 |
Angle is the rotation angle, in degrees, of the template at the current match
location.
|
 |
Scale is the ratio of the size of the matched template relative to the original
template image, expressed as a percentage.
|
 |
Score ranks the match results on a scale of 0 to 1000, where 0 equals no match
and 1000 equals a perfect match.
|
 |
Bounding Box is an array of five points that define the boundary of the template.
|
 |
Contrast Reversed specifies whether the match is an inverse of the template image. This parameter is TRUE if the match is an inverse of the template image. For example, the match is a white object on a black background but the template image is a black object on a white background. This parameter is FALSE if the match is not the inverse of the template image.
|
 |
Occlusion % is the percentage of the match that is occluded.
|
 |
Template Target Curve Score specifies how closely the curves in the match region of the inspection, or
target, image match the curves in the template. Score values can range from 0 to 1000, where a score of 1000 indicates that all template curves have a corresponding curve in the match region of the inspection image.
|
 |
Target Template Curve Score specifies how closely the curves in the match region of the inspection, or target, image match the curves in the template. Score values can range from 0 to 1000, where a score of 1000 indicates that all curves in the match region of the inspection image have a corresponding curve in the template image.
|
 |
Correlation Score specifies the accuracy of the match obtained by comparing the template image to the match region using a correlation metric that compares the two regions as a function of their pixel values. A score of 1000 indicates a perfect match, and a score of 0 indicates no match.
|
|
 |
Number of Matches is the number of template matches found in the inspection image based on
the input settings.
|
 |
error out contains error information. If error in
indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error
out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status
that this VI or function produces. Right-click the error out
indicator on the front panel and select Explain Error from the
shortcut menu for more information about the error.
 |
status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred or FALSE (checkmark) to indicate a warning
or that no error occurred.
|
 |
code is the error or warning code. If status is
TRUE, code is a nonzero error code. If status is FALSE, code is 0 or a warning code.
|
 |
source describes the origin of the error or warning and is, in most cases, the
name of the VI or function that produced the error or warning. The default is an empty
string.
|
|