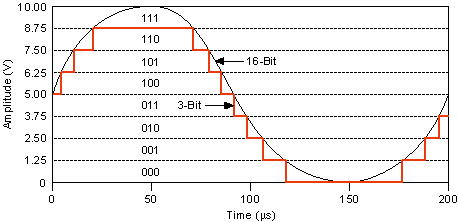
DAC Resolution
Digital-to-analog converter (DAC) resolution is a limiting factor in determining the accuracy of the re–creation of an analog waveform from digital samples. More details are present in the waveform if the DAC resolution is increased. A 3-bit DAC divides its vertical range into eight discrete levels. With a vertical range of 10 V, the 3-bit DAC cannot generate voltage differences smaller than 1.25 V. In comparison, a 16-bit DAC with 65,536 discrete levels can generate voltage differences as small as 153 µV.
The following figure shows the difference between two waveforms. The 16-bit waveform looks like a continuous sine wave, but if you were to zoom in, you would see the discrete steps of 153 µV. Both waveforms are composed of discrete voltage steps, but the 16-bit version looks much closer to a "pure" continuous–time sine waveform.