7.11.1 Object Maintenance Concepts
The LANSA object security system can be used to control access to specific LANSA objects:
- Fields (and Forms, Reusable Parts and WAMs when relating to them on an IBM i)
Implementing security at an object level is optional and can be a significant administrative overhead.
Function level security should be used with care as this involves more run time security checking and consequently uses more system resources.
If using an IBM i Master, the Use Function level security option in the Execution and Security Settings window must be set to Y, indicate that function level security is required.
|
If using a Visual LANSA Master, right click on an object in the Repository to select the Security Settings for that object.
Access to all of objects is controlled by the LANSA Object Maintenance system.
|
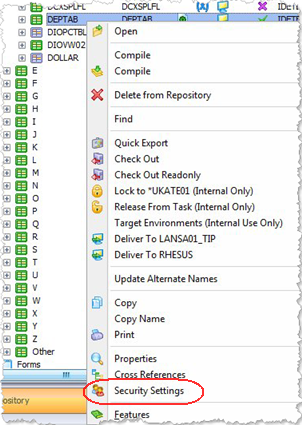
|
|
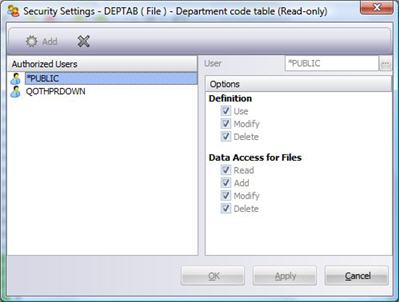
Within the LANSA security system there are 2 "classes" of access associated with most object types. These are:
DEFINITION
This class of access is applicable to fields, files, processes, functions, partitions, templates, system variables, weblets and multilingual variables. This access controls a users' right to USE, MODIFY and DELETE the definition of an object.
DATA Access for Files
This class of access is only applicable to files. This access controls a users right to READ, ADD, MODIFY or DELETE information (records) contained in the file.
|
|
Refer to 7.1.5 Execution and Security for security setting information.
The two object classes (DEFINITION and DATA) and the way they affect the object types is summarized in the following table.
|
Object Type
|
Access Class
|
Description Of Access Allowable
|
|
FIELD
COMPONENT
WAM
|
DEF
|
USE: User can use the field definition.
MODIFY: User can modify the field definition.
DELETE: User can delete the field definition.
|
|
DATA
|
Data rights are not applicable.
|
|
FILE
|
DEF
|
USE: User can use the file definition.
MODIFY: User can modify the file definition.
DELETE: User can delete the file definition.
|
|
DATA
|
READ: User can read records from the file.
ADD: User can add records to the file.
CHANGE: User can change records in the file
DELETE: User can delete records from the file.
|
|
PROCESS or FUNCTION
|
DEF
|
USE: User can use (run) the process/function.
MODIFY: User can change the definition.
DELETE: User can delete the definition.
|
|
DATA
|
Data rights are not applicable.
|
|
PARTITION
|
DEF
|
USE: User can access the partition.
MODIFY: User can change the partition definition.
DELETE: User can delete the partition definition.
|
|
DATA
|
Data rights are not applicable.
|
|
TEMPLATE
|
DEF
|
USE: User can use the template.
MODIFY: User can change the template definition.
DELETE: User can delete the template definition.
|
|
DATA
|
Data rights are not applicable.
|
|
SYSTEM VARIABLE
|
DEF
|
USE: User can use the system variable.
MODIFY: User can change the system variable.
DELETE: User can delete the system variable.
|
|
DATA
|
Data rights are not applicable.
|
|
MULTILINGUAL VARIABLE
|
DEF
|
USE: User can use the multilingual variable.
MODIFY: User can change the multilingual variable.
DELETE: User can delete the multilingual variable.
|
|
DATA
|
Data rights are not applicable.
|
|
WEBLET
|
DEF
|
USE: User can use the weblet.
MODIFY: User can change the weblet.
DELETE: User can delete the weblet.
|
|
DATA
|
Data rights are not applicable.
|
|
Also See
7.9 User and Security Maintenance
Ý 7.11 Object Maintenance

