Resistance
The NI 4065 and NI 4070/4071/4072 make resistance measurements using a constant-current technique. A current is supplied to the resistance under test, and the DMM measures the resulting voltage as represented in the following figure.
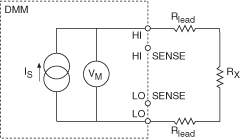
With a known current and voltage, the DMM can determine resistance using Ohm's Law, as follows:
VM = IsRT
where RT is the sum of all resistances
RT = Rx + RLEAD + RLEAD
Therefore, the value of Rx = VM/Is if RLEAD is small or negligible compared to Rx.
The NI 4070/4071/4072 generates a highly-stable current source, Is. The table below lists the value of this current by range:
| Range | Test Current1 | Maximum Test Voltage (Vt) | Offset Compensated Ohms Available? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 Ω | 1 mA | 100 mV | Yes |
| 1 kΩ | 1 mA | 1 V | Yes |
| 10 kΩ | 100 µA | 1 V | Yes |
| 100 kΩ | 10 µA | 1 V | No |
| 1 MΩ | 10 µA | 10 V | No |
| 10 MΩ | 1 µA | 10 V | No |
| 100 MΩ | 1 µA || 10 MΩ* | 10 V | No |
| 5 GΩ | 1 µA || 10 MΩ* | 10 V | No |
| 1-10% to 0% tolerance *Refer to Measuring on the 100 MΩ Range. | |||
All ranges except the 100 MΩ range and the 5 GΩ range (NI 4071) have greater than 10 GΩ input resistance. The 100 MΩ range and the 5 GΩ range (NI 4071) use a 10 MΩ input resistance.
Every time you run self-calibration, the current source recalibrates to an ultra-high stability 10 kΩ reference resistor. While the absolute tolerance of the current is ±5%, the recalibration process identifies the value to a sub-ppm precision level. The calculated value of resistance is corrected to the precision of the ultra-stable reference resistor, assuring accurate measurements.
The NI 4070/4071/4072 has two modes of resistance measurement: 2-wire and 4-wire. Each mode applies the same precision current to the circuit, but the difference between 2-wire and 4-wire resistance measurements is how the voltage measurement is made.
The NI 4065 generates a highly-stable current source, Is. The table below lists the value of this current by range:
| Range | Test Current1 | Maximum Test Voltage (Vt) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 Ω | 1 mA | 100 mV |
| 1 kΩ | 1 mA | 1 V |
| 10 kΩ | 100 µA | 1 V |
| 100 kΩ | 10 µA | 1 V |
| 1 MΩ | 5 µA | 5 V |
| 10 MΩ | 500 nA | 5 V |
| 100 MΩ | 500 nA || 10 MΩ* | 5 V |
| 1-10% to 0% tolerance *Refer to Measuring on the 100 MΩ Range. | ||
The NI 4065 has two modes of resistance measurement: 2-wire and 4-wire. Each mode applies the same precision current to the circuit, but the difference between 2-wire and 4-wire resistance measurements is how the voltage measurement is made.