DC Voltage
The NI 4065 and NI 4070/4071/4072 can measure signals in the sub-microvolt range. To take accurate low-voltage measurements with confidence, consider the following factors: thermal voltages, selectable input resistance, and input bias current.
Selectable Input Resistance
You can select the NI 4065 and NI 4070/4071/4072 DCV input resistance to optimize measurement performance in situations where large source resistance is present. In the following figure, S1 is used to select a 10 MΩ input resistance on the 0.1 V, 1 V, and 10 V DC ranges.
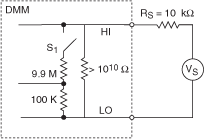
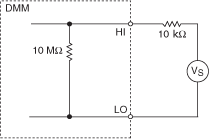
The following figure shows an equivalent circuit after the 10 MΩ input resistance has been selected:
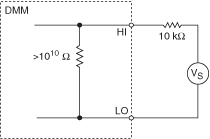
The following figure shows an equivalent circuit after the 10 GΩ input resistance has been selected:
The following table lists the available NI 4070/4071/4072 input resistance selections. NI calibrates the NI 4070/4071/4072 for full accuracy with all input resistances shown.
 |
Note The default input resistance for each range is italicized. |
| DCV | ACV | Waveform Acquisitions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Input Resistance | Range | Input Resistance | Range | Input Resistance |
| 100 mV | 10 MΩ or 10 GΩ | 50 mV | 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 MΩ (NI 4071) | 100 mV | 10 GΩ or 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 GΩ or 10 MΩ (NI 4071) |
| 1 V | 10 MΩ or 10 GΩ | 500 mV | 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 MΩ (NI 4071) | 1 V | 10 GΩ or 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 MΩ (NI 4071) |
| 10 V | 10 MΩ or 10 GΩ | 5 V | 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 MΩ (NI 4071) | 10 V | 10 GΩ or 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 MΩ (NI 4071) |
| 100 V | 10 MΩ | 50 V | 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 MΩ (NI 4071) | 100 V | 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072); 10 MΩ (NI 4071) |
| 300 V | 10 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072) | 300 V | 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072) | 300 V | 1 MΩ (NI 4070, NI 4072) |
| 1000 V | 10 MΩ (NI 4071) | 700 V | 10 MΩ (NI 4071) | 1000 V | 10 MΩ (NI 4071) |
The following table lists the available NI 4065 input resistance selections. NI calibrates the NI 4065 for full accuracy with all input resistances shown.
 |
Note The default input resistance for each range is italicized. |
| DCV | ACV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Input Resistance | Range | Input Resistance |
| 100 mV | 10 MΩ or 10 GΩ | 200 mV | 10 MΩ |
| 1 V | 10 MΩ or 10 GΩ | 2 V | 10 MΩ |
| 10 V | 10 MΩ or 10 GΩ | 20 V | 10 MΩ |
| 100 V | 10 MΩ | 300 V | 10 MΩ |
| 300 V | 10 MΩ | ||
Input Bias Current
If the source resistance is greater than 10 kΩ, then you may need to include the effects of input bias current in addition to input resistance. For example, for 100 kΩ source resistance, a 100 pA bias current creates an offset error of 10 µV, as shown in the following figure.
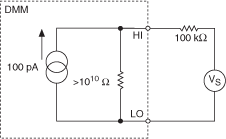
With an input resistance of >10 GΩ selected, most of the input bias current flows through the source resistance (100 kΩ), causing an offset voltage.
DMM input bias current approximately doubles for every 10 ºC of environmental temperature change. For example, an input bias current of 25 pA at 23 ºC translates to about 50 pA at 33 ºC, 100 pA at 43 ºC, and so on. Likewise, as temperature is decreased, the current drops 50% for every 10 ºC. Thus, at 13 ºC, the input bias current is approximately 12.5 pA.