DC Noise Rejection for Waveforms
The DC Noise Rejection feature that can reduce noise in DC measurements in DMM mode can also be used to alter the noise and frequency response of waveform acquisitions. Three settings of the DC Noise Rejection parameter are available: normal, second order, and high order. You can specify the noise rejection settings using a property node, as for DMM-mode readings.
Only Normal DC Noise Rejection is available for sampling rates above 200,000 S/s.
Normal
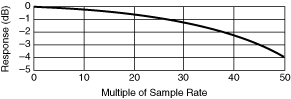
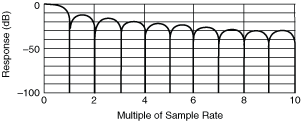
Normal DC Noise Rejection gives rise to notches in the frequency response at multiples of the sampling rate, and the response is attenuated by 4 dB at half the sampling rate, in addition to any attenuation present at the maximum sampling rate of 1.8 MS/s. For example, with a selected sampling rate of 1 kS/s, response is down 4 dB at 500 Hz, shown in the first following graph, and is 0 at multiples of 1 kHz as shown in the second graph.
Second Order
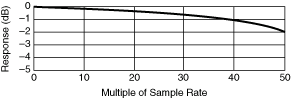
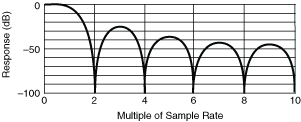
Second order DC Noise Rejection gives rise to notches in the frequency response at even multiples of the sampling rate, and the response is attenuated by 1.9 dB at half the sampling rate, in addition to any attenuation present at the maximum sampling rate of 1.8 MS/s. For example, with a selected sampling rate of 1 kS/s, response is down 1.9 dB at 500 Hz, shown in the first following graph, and is 0 at multiples of 2 kHz as shown in the following graph.
High Order
High order DC Noise Rejection gives rise to high attenuation to frequencies above about 4 times the sampling rate, and the response is attenuated by 0.7 dB at half the sampling rate, in addition to any attenuation present at the maximum sampling rate of 1.8 MS/s. For example, with a selected sampling rate of 1 kS/s, response is down 0.7 dB at 500 Hz, shown in the first following graph, and is very small at frequencies above 4 kHz as shown in the second following graph:
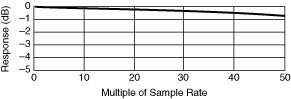
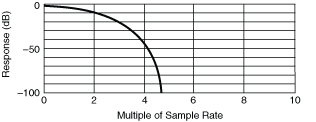
Other Considerations
The default DC Noise Rejection setting is Normal, and it gives the lowest noise at very low frequencies. However, it does not reject out-of-band signals very well and has considerable attenuation at half the sample rate. It also yields a non-flat noise spectrum due to the notches at multiples of the sample rate. Second order DC Noise Rejection gives the lowest overall noise over a broad range of sampling rates, roughly from 500 S/s to 100 kS/s. It does a better job rejecting out-of-band signals, while reducing in-band attenuation, and it yields a flat noise spectrum. High-order DC Noise Rejection offers the flattest in-band frequency response and is useful for rejecting strong out-of-band noise signals. It also yields a flat noise spectrum. However, it yields higher overall noise than second order DC Noise Rejection.