Thermocouples

Thermocouples consist of a pair of dissimilar metals that meet at a contact point, which produces a small, open-circuit voltage that corresponds to temperature. This thermoelectric voltage is known as Seebeck voltage and is nonlinear with respect to temperature.
This voltage is converted to temperature using tables of coefficients and the following polynomial scaling function:
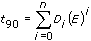
where t90 is the temperature in degrees Celsius, E is the voltage in millivolts, and Di is the coefficient.
The NI 4065/4070/4071/4072 support temperature measurements with J, K, N, T, E, R, S, and B type thermocouples, The driver software contains all necessary coefficient tables to perform the ITS-90 polynomial scaling.
Thermocouple types differ in composition and accurate range as illustrated in the following table:
| Thermocouple Type | Positive Conductor | Negative Conductor | Temperature Range (°C) | Extended Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | Iron | Constantan | –150 to 1200 | –210 to –150 |
| K | Chromel | Alumel | –100 to 1200 | –200 to –100 |
| N | Nicrosil | Nisil | –100 to 1300 | –200 to –100 |
| T | Copper | Constantan | –100 to 400 | –200 to –100 |
| E | Chromel | Constantan | –150 to 1000 | –200 to –150 |
| R | Platinum-13% Rhodium | Platinum | 300 to 1760 | –50 to 300 |
| S | Platinum-10% Rhodium | Platinum | 400 to 1760 | –50 to 400 |
| B | Platinum | Rhodium | 1100 to 1820 | 400 to 1100 |
Reference Junction
Thermocouple measurements require a user-specified fixed reference junction temperature. This is also referred to as the "cold-junction compensation" or "CJC" temperature. If the user does not specify a reference junction temperature, a default of 25 °C is assumed.
NI-DMM provides the Measure Temperature (Thermocouple) example, which you can find by using the shortcut at Start»All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DMM»Examples.
In many applications, the reference junction temperature is measured by a separate temperature sensor (typically an RTD or thermistor) to improve thermocouple measurement accuracy.
Cabling
Thermocouples are cabled using the HI and LO connectors of the DMM. The polarity of the thermocouple leads is critical for correct thermocouple measurements.
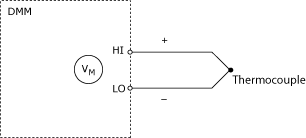
You must use a thermocouple adapter to connect a thermocouple to your DMM.
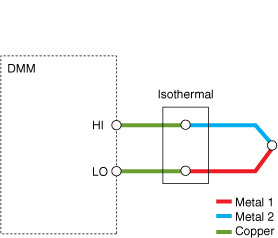
Thermocouples require some form of temperature reference to compensate for unwanted parasitic thermocouples. This process is called cold-junction compensation.
Underlying DMM Measurement
To measure temperature with any thermocouple, the DMM internally performs a DC Voltage measurement with the range, resolution, timing, and other measurement options that have been specified by the user. The resulting voltage is then converted to degrees Celsius by software using ITS-90 polynomial scaling.
When configuring a temperature transducer measurement, the user must specify the range and resolution of the underlying voltage or resistance measurement while configuring the DMM. The recommended range for thermocouples is 100 mV
 |
Note For more information on taking thermocouple temperature measurements, refer to the NI Developer Zone document, Taking Thermocouple Temperature Measurements. |