SimpleAdapter
|
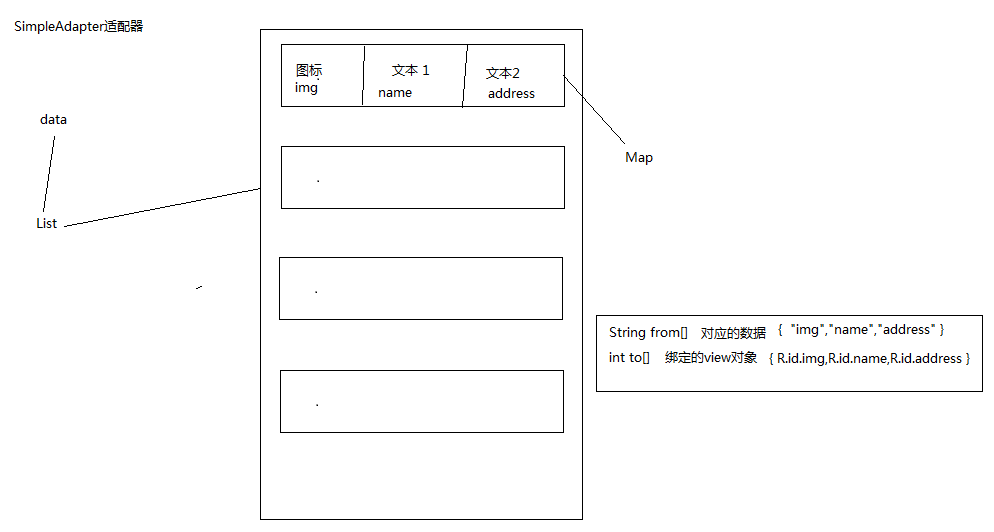
SimpleAdapter:一行显示的数据有图标,文本等信息。 SimpleAdapter(Context context, List<? extends Map<String, ?>> data,int resource, String[] from, int[] to)
context
上下文
data
每行数据是一个map,一列对应一个key,多行数据为一个list
resource
资源文件
from
和map中的key相对应
to
和from列对应的id
 |
|
演示: 1、layout_item.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iv"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/emo_im_tongue_sticking_out"
android:contentDescription="tupian"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_text1"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_text2"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
2、MainActivity.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ListView lv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
lv = (ListView) this.findViewById(R.id.lv);
List<Map<String, Object>> data = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
HashMap<String, Object> map1 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map1.put("img", R.drawable.emo_im_tongue_sticking_out);
map1.put("name", "hacket");
map1.put("address", "永州");
HashMap<String, Object> map2 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map2.put("img", R.drawable.emo_im_undecided);
map2.put("name", "xiaosheng");
map2.put("address", "深圳");
HashMap<String, Object> map3 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map3.put("img", R.drawable.emo_im_winking);
map3.put("name", "小胜");
map3.put("address", "北京");
data.add(map1);
data.add(map2);
data.add(map3);
String[] from = { "img", "name", "address" };
int[] to = { R.id.iv, R.id.tv_text1, R.id.tv_text2 };
lv.setAdapter(new SimpleAdapter(this, data, R.layout.layout_item, from,to));
/*
* data : 每一行数据是一个map,多行数据放到一个
list中
* resource 资源文件xml
* from A list of column names that will be added to the Map associated with each item.
一系列的names,这些将被加到map集合中去的,也就是map的key
* to 每一列要显示的数据的id,要和from中的列资源对应起来
*/
}
}
3、效果:
 |