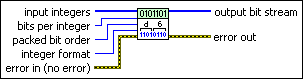
MT UnPack Bits VI
Unpacks an array of signed or unsigned integer data. You can specify the packed bit order as MSB First or LSB First. You can also specify the integer format to be Signed or Unsigned.
This array unpacks data of the form an,n = 0…N–1 into an output binary bit stream {b i}, i = 0… MN – 1, where M denotes the number of bits per integer.
 |
input integers specifies the signed or unsigned integer data a n, n=0…N–1 to be converted into binary data. The default is empty. |
||||||
 |
bits per integer specifies the number of bits corresponding to the binary representation of every element in the input integers array. If you choose Unsigned for the integer format, the maximum value is 31. If you choose Signed, the maximum value is 32.The default is 1. |
||||||
 |
packed bit order specifies the order in which the binary data stream has been packed into integers.
|
||||||
 |
integer format specifies the input integer format.
|
||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||
 |
output bit stream returns the output binary data stream b i ={0,1}, i=0…MN–1 that corresponds to the packed representation of the input binary data. |
||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Details
The relationship between the input integers and the output bit stream is given by the following equations:
b i×M+j = (a i»(M–1–j)) &1, j = 0…M–1, i=0…N – 1 (packed bit order set to MSB First)
b i×M+j= (a i»j) &1, j = 0…M – 1, i=0…N – 1 (packed bit order set to LSB First)
Where » denotes the operation of right shifting, and the operator & stands for the logical AND operation. For example, assume the input integers array is the element [4], the bits per integer value is specified as 3, and integer format is set to Unsigned. If packed bit order is set to MSB First, the output bit stream is [1 0 0]. If the packed bit order is set to LSB first, the output bit stream is [0 0 1]. The signed negative numbers are stored as the 2's complement. Thus, if integer format is set to Signed and the bits per integer is set to 3, the input integer array is the element [–3], and the packed bit order is set to MSB First the output bit stream is [1 0 1].