MT Generate Synchronization Parameters VI
Constructs an FSK, PSK, QAM, MSK, PAM, ASK, or CPM synchronization parameters cluster that you can pass to a demodulation VI, using an array of either synchronization bits or synchronization numbers. The generated synchronization parameters cluster avoids phase ambiguity at the demodulator, thus allowing recovery of the actual message bits.
If the synchronization parameter passed to the demodulation VI is left empty, the constellation of the demodulated waveform has a 90° carrier phase ambiguity for two-dimensional modulation schemes (QAM, QPSK and higher order PSK) and a 180° carrier phase ambiguity for one-dimensional modulation schemes (PAM/ASK/BPSK).
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
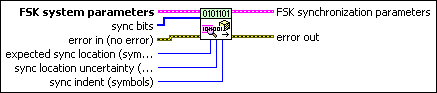
MT Generate FSK Synchronization Parameters (bit array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for FSK demodulation using a synchronization sequence directly represented by the sync bits input array.
 |
FSK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the FSK system. Wire the FSK system parameters cluster returned by the FSK (M) or FSK (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||||||
 |
sync bits specifies an array of synchronization bits used to generate the FSK synchronization parameter cluster. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can wire a 16-bit array with the above entries to the sync bits parameter. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. The default is 10. |
||||||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||||||
 |
FSK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
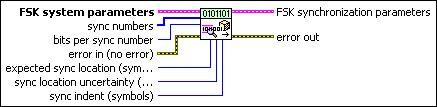
MT Generate FSK Synchronization Parameters (number array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for FSK demodulation using a synchronization sequence defined by a sync numbers array in which each number represents a group of bits.
 |
FSK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the FSK system. Wire the FSK system parameters cluster returned by the FSK (M) or FSK (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||||||
 |
sync numbers specifies an array of synchronization numbers in which the binary representation of each number is used to generate the sync bit array. By default, the internal conversion of each sync number into the corresponding synchronization bit sequence is performed with the most significant bit first (left-aligned) approach. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can specify sync numbers as an array with a single element xFFFE. Specify the bits per sync number value in this case to be 16. You can also specify sync numbers as an array of two elements (xFF and xFE), and specify the bits per sync number value as 8. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||||||
 |
bits per sync number specifies the number of bits corresponding to each sync number in the sync numbers array. The default is 32. |
||||||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. The default is 10. |
||||||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||||||
 |
FSK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
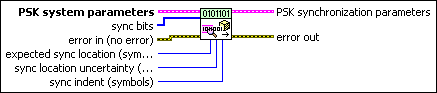
MT Generate PSK Synchronization Parameters (bit array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for PSK demodulation using a synchronization sequence directly represented by the sync bits array.
 |
PSK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the PSK system. Wire the PSK system parameters cluster of the PSK (M) or PSK (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
sync bits specifies an array of synchronization bits used to generate the PSK synchronization parameter cluster. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can wire a 16-bit array with the above entries to the sync bits parameter. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. The default is 10. |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
PSK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
MT Generate PSK Synchronization Parameters (number array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for PSK demodulation using a synchronization sequence defined by a sync numbers array in which each number represents a group of bits.
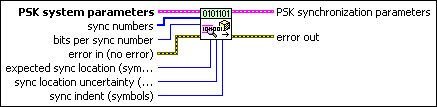
 |
PSK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the PSK system. Wire the PSK system parameters cluster of the PSK (M) or PSK (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
sync numbers specifies an array of synchronization numbers in which the binary representation of each number is used to generate the sync bit array. By default, the internal conversion of each sync number into the corresponding synchronization bit sequence is performed with the most significant bit first (left-aligned) approach. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can specify sync numbers as an array with a single element xFFFE. Specify the bits per sync number value in this case to be 16. You can also specify sync numbers as an array of two elements (xFF and xFE), and specify the bits per sync number value as 8. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
bits per sync number specifies the number of bits corresponding to each sync number in the sync numbers array. The default is 32. |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. The default is 10. |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
PSK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
MT Generate QAM Synchronization Parameters (bit array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for QAM demodulation using a synchronization sequence directly represented by the sync bits array.
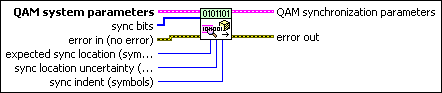
 |
QAM system parameters specifies parameter values defining the QAM system. Wire the QAM system parameters cluster returned by the QAM (M) or QAM (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync bits specifies an array of synchronization bits used to generate the QAM synchronization parameter cluster. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can wire a 16-bit array with the above entries to the sync bits parameter. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. The default is 10. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
QAM synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
MT Generate QAM Synchronization Parameters (number array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for QAM demodulation using a synchronization sequence defined by a sync numbers array in which each number represents a group of bits.
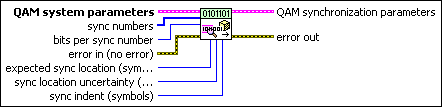
 |
QAM system parameters specifies parameter values defining the QAM system. Wire the QAM system parameters cluster returned by the QAM (M) or QAM (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync numbers specifies an array of synchronization numbers in which the binary representation of each number is used to generate the sync bit array. By default, the internal conversion of each sync number into the corresponding synchronization bit sequence is performed with the most significant bit first (left-aligned) approach. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can specify sync numbers as an array with a single element xFFFE. Specify the bits per sync number value in this case to be 16. You can also specify sync numbers as an array of two elements (xFF and xFE), and specify the bits per sync number value as 8. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
bits per sync number specifies the number of bits corresponding to each sync number in the sync numbers array. The default is 32. |
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
QAM synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
MT Generate MSK Synchronization Parameters (bit array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for MSK demodulation using a synchronization sequence directly represented by the sync bits input array.
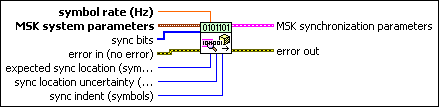
 |
sync bits specifies an array of synchronization bits used to generate the MSK synchronization parameter cluster. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can wire a 16-bit array with the above entries to the sync bits parameter. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
symbol rate specifies the desired symbol rate, in hertz. The default is 1.0. |
||||||||
 |
MSK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the MSK system. Wire the MSK system parameters cluster returned by the MSK instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
MSK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
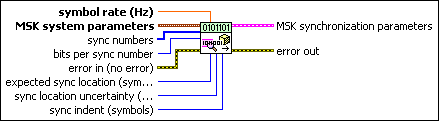
MT Generate MSK Synchronization Parameters (number array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for MSK demodulation using a synchronization sequence defined by a sync numbers input array in which each number represents a group of bits.
 |
sync numbers specifies an array of synchronization numbers in which the binary representation of each number is used to generate the sync bit array. By default, the internal conversion of each sync number into the corresponding synchronization bit sequence is performed with the most significant bit first (left-aligned) approach. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can specify sync numbers as an array with a single element xFFFE. Specify the bits per sync number value in this case to be 16. You can also specify sync numbers as an array of two elements (xFF and xFE), and specify the bits per sync number value as 8. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
bits per sync number specifies the number of bits corresponding to each sync number in the sync numbers array. The default is 32. |
||||||||
 |
symbol rate specifies the desired symbol rate, in hertz. The default is 1.0. |
||||||||
 |
MSK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the MSK system. Wire the MSK system parameters cluster returned by the MSK instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
MSK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
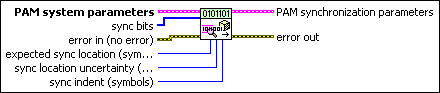
MT Generate PAM Synchronization Parameters (bit array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for PAM demodulation using a synchronization sequence directly represented by the sync bits input array.
 |
PAM system parameters specifies parameter values defining the PAM system. Wire the PAM system parameters cluster returned by the PAM (M) or PAM (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync bits specifies an array of synchronization bits used to generate the PAM synchronization parameter cluster. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can wire a 16-bit array with the above entries to the sync bits parameter. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
PAM synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
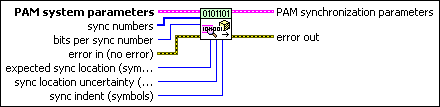
MT Generate PAM Synchronization Parameters (number array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for PAM demodulation using a synchronization sequence defined by a sync numbers input array in which each number represents a group of bits.
 |
PAM system parameters specifies parameter values defining the PAM system. Wire the PAM system parameters cluster returned by the PAM (M) or PAM (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync numbers specifies an array of synchronization numbers in which the binary representation of each number is used to generate the sync bit array. By default, the internal conversion of each sync number into the corresponding synchronization bit sequence is performed with the most significant bit first (left-aligned) approach. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can specify sync numbers as an array with a single element xFFFE. Specify the bits per sync number value in this case to be 16. You can also specify sync numbers as an array of two elements (xFF and xFE), and specify the bits per sync number value as 8. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
bits per sync number specifies the number of bits corresponding to each sync number in the sync numbers array. The default is 32. |
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
PAM synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
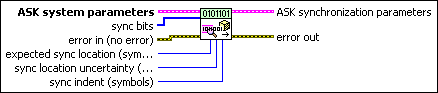
MT Generate ASK Synchronization Parameters (bit array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for ASK demodulation using a synchronization sequence directly represented by the sync bits array.
 |
ASK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the ASK system. Wire the ASK system parameters cluster returned by the ASK instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync bits specifies an array of synchronization bits used to generate the ASK synchronization parameter cluster. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can wire a 16-bit array with the above entries to the sync bits parameter. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
ASK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
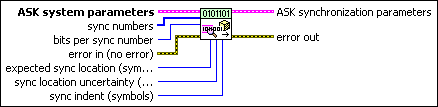
MT Generate ASK Synchronization Parameters (number array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for ASK demodulation using a synchronization sequence defined by a sync numbers array in which each number represents a group of bits.
 |
ASK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the ASK system. Wire the ASK system parameters cluster returned by the ASK instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync numbers specifies an array of synchronization numbers in which the binary representation of each number is used to generate the sync bit array. By default, the internal conversion of each sync number into the corresponding synchronization bit sequence is performed with the most significant bit first (left-aligned) approach. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can specify sync numbers as an array with a single element xFFFE. Specify the bits per sync number value in this case to be 16. You can also specify sync numbers as an array of two elements (xFF and xFE), and specify the bits per sync number value as 8. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
bits per sync number specifies the number of bits corresponding to each sync number in the sync numbers array. The default is 32. |
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
ASK synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
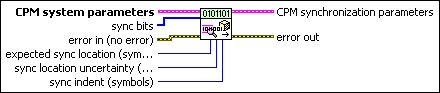
MT Generate CPM Synchronization Parameters (bit array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for CPM demodulation using a synchronization sequence directly represented by the sync bits array.
 |
CPM system parameters specifies parameter values defining the CPM system. Wire the CPM system parameters cluster from the CPM (M) or CPM (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync bits specifies an array of synchronization bits used to generate the CPM synchronization parameter cluster. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can wire a 16-bit array with the above entries to the sync bits parameter. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the synchronization parameters in symbols. Set this value to –1 to search the entire waveform for the synchronization symbols. The default is –1. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. The default is 10. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. The default is 0. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
CPM synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
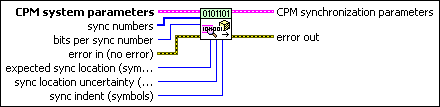
MT Generate CPM Synchronization Parameters (number array)
This polymorphic instance generates synchronization parameters for CPM demodulation using a synchronization sequence defined by a sync numbers array in which each number represents a group of bits.
 |
CPM system parameters specifies parameter values defining the CPM system. Wire the CPM system parameters cluster from the CPM (M) or CPM (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||
 |
sync numbers specifies an array of synchronization numbers in which the binary representation of each number is used to generate the sync bit array. By default, the internal conversion of each sync number into the corresponding synchronization bit sequence is performed with the most significant bit first (left-aligned) approach. For example, if you specify a preamble word of 1111 1111 1111 1110 for symbol synchronization, you can specify sync numbers as an array with a single element xFFFE. Specify the bits per sync number value in this case to be 16. You can also specify sync numbers as an array of two elements (xFF and xFE), and specify the bits per sync number value as 8. For reliable symbol synchronization, specify an array of length (10 × bits per symbol). The default is 0.
|
||||||||
 |
bits per sync number specifies the number of bits corresponding to each sync number in the sync numbers array. The default is 32. |
||||||||
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the first symbol of the synchronization sequence. This value is an index to the input complex waveform. A value of -1 searches the entire input complex waveform and ignores the sync location uncertainty parameter. |
||||||||
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1. |
||||||||
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols. |
||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||
 |
CPM synchronization parameters returns synchronization parameters to pass to the demodulation VI.
|
||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|






 /M each
symbol.
/M each
symbol.