MT Modulate FSK VI
Receives a sequence of data bits, performs FSK modulation, and returns the modulated complex baseband waveform in the output complex waveform parameter.
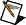 |
Note Using FIR pulse-shaping filters in modulation VIs may lead to the apparent loss of bits caused by filter delay. Refer to Filter Delay for more information about this effect. Set the flush buffers? parameter to TRUE to offset the effects of filter delay in single-shot operations or in the last iteration of continuous operations. |
 |
input bit stream specifies the sequence of information bits to be modulated.
|
||||||||||
 |
FSK system parameters specifies parameter values defining the FSK system. Wire the FSK system parameters cluster returned by the FSK (M) or FSK (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
|
||||||||||
 |
symbol rate specifies the desired symbol rate, in hertz. The default is 1.0. |
||||||||||
 |
pulse shaping filter coefficients specifies an ordered array containing the desired pulse-shaping coefficients. Wire the pulse shaping filter coefficients parameter of the MT Generate Filter Coefficients VI to this parameter. When generating the filter coefficients, ensure that the value of the pulse shaping samples per symbol parameter of the MT Generate Filter Coefficients VI is equal to the value of the samples per symbol element of the FSK system parameters cluster passed to this VI.
|
||||||||||
 |
reset? specifies whether the VI continues modulation using the previous iteration states. The VI resets on the first call and when reset? is set to TRUE. reset? must be set to TRUE whenever you want to restart the modulator. The default is TRUE. |
||||||||||
 |
flush buffers? forces out samples from the modulated waveform that are affected by the FIR pulse-shaping filter delay. Set this parameter to TRUE during single-shot operations and during the last iteration of continuous operations. The default is FALSE.
|
||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
||||||||||
 |
output complex waveform returns the FSK-modulated complex baseband waveform data.
|
||||||||||
 |
symbols out returns the array of mapped symbols, before pulse shaping is applied. The real portion corresponds to the carrier frequency offset of the mapped symbol, and the imaginary portion is zero. |
||||||||||
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Details
The bandwidth of a CPM signal, using Carson’s Rule, is approximately given by the following formula:
BW = 2(Fm + Fd)
where
Fm is symbol bandwidth and is given by (1 + 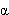 ) * R, where R is the symbol rate and
) * R, where R is the symbol rate and 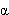 is the filter parameter
is the filter parameter
Fd is the maximum frequency deviation
The sample rate of the signal is given by fs = samples per symbol * R.
A value of fs that is less than BW causes aliasing. Refer to the Aliasing topic in the LabVIEW Help for more information about aliasing.
The signal can be checked for aliasing by observing its spectrum and noting whether the observed bandwidth of the signal is higher than the calculated bandwidth.
You can prevent your signal from aliasing by using one of the following strategies:
- Increasing the sample rate by increasing the samples per symbol.
- Decreasing the bandwidth of the message signal by decreasing the filter parameter
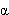 .
. - Decreasing the maximum modulation index (hi).