|
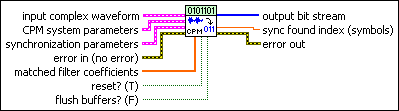
input complex waveform specifies the CPM-modulated complex baseband waveform data.
 |
t0 specifies the trigger (start) time of the Y array. The default is 0.0.
|
 |
dt specifies the time interval between data points in the Y array. The default is 1.0.
|
 |
Y specifies the complex-valued signal-only baseband modulated
waveform. The real and imaginary parts of this complex data array correspond to
the in-phase (I) and quadrature-phase (Q) data, respectively.
|
|
 |
CPM system parameters specifies parameter values defining the CPM system. Wire the CPM system parameters cluster from the CPM (M) or CPM (Map) instance of the MT Generate System Parameters VI to this cluster. Do not alter the values.
 |
samples per symbol specifies an even, positive number of samples dedicated to
each symbol. Multiply this value by the symbol rate to determine the sample
rate. The default is 16.
 |
Note The Modulation Toolkit demodulation and detector VIs use timing recovery, which is optimized for four or more samples per symbol. |
|
 |
symbol map specifies the number of samples per symbol in the modulated
output complex waveform. It should be an even number.
|
|
 |
matched filter coefficients specifies an ordered array containing the desired matched filter coefficients. Wire the matched filter coefficients parameter of the MT Generate Filter Coefficients VI to this parameter. When generating the filter coefficients, ensure that the value of the matched samples per symbol parameter of the MT Generate Filter Coefficients VI is equal to the value of the samples per symbol element of the CPM system parameters parameter in this VI.
 |
Note
When reset? is set to TRUE, there is a transient response of half the filter length at the start of the demodulated signal, and the returned data is shortened by approximately half the filter length. When reset? is set to FALSE, the VI uses data from the previous iteration to prime the filter, hence eliminating the transient. |
 |
Tip
When reset? is set to TRUE, the number of trailing symbols that are carried over to the next iteration during demodulation is upper bounded by [L/2 + P/2 + 4(13 + K)]/K , where L is the matched filter length in taps, P is the pulse-shaping filter length in taps, and K is the number of samples per symbol. For typical values of L = 57, P = 25, and K = 4, this value equals 27.25 symbols. Therefore when reset? is set to TRUE, a total of 1,028 CPM symbols must be sent to the demodulator to obtain at least 1,000 symbols at the output. This formula does not account for truncation due to any specified synchronization parameters.
|
|
 |
synchronization parameters specifies parameter values describing the synchronization sequence and the range of bits over which to search for the sequence. Wire the CPM synchronization parameters cluster returned by the CPM bit array or number array instances of the MT Generate Synchronization Parameters VI to this cluster.
 |
Note If the CPM synchronization parameters cluster is not wired, the demodulator does not attempt to synchronize, and the constellation of the demodulated waveform has a carrier phase ambiguity. |
 |
expected sync location specifies the expected location of the first symbol of the synchronization sequence. This value is an index to the input complex waveform. A value of -1 searches the entire input complex waveform and ignores the sync location uncertainty parameter.
|
 |
sync sequence specifies the mapped symbol pattern. Although the data type is complex, only the real portion is used. For
CPM, the real portion of the mapped symbols is the frequency deviation of the symbol
value, and the imaginary portion is 0. To prevent false synchronization, configure this pattern so that there is a low probability of accidental correlation to nonsynchronized parts of the data stream. If this parameter is left empty, the signal is still demodulated.
|
 |
sync location uncertainty specifies the number of symbols before or after the expected sync location where the first symbol of
the sync sequence may be located. This parameter is
ignored if the expected sync location parameter is set to -1.
|
 |
sync indent specifies the distance that the sync sequence is indented into the information block. The distance is the number of demodulated symbols preceding the sync sequence. For example, a value of 10 indicates that the output bit stream consists of 10 data symbols, followed by the sync sequence, followed by the remaining data symbols.
|
|
 |
reset? (T) specifies an ordered array containing the desired pulse-shaping coefficients. This parameter is used internally to reproduce the ideal waveform for making measurements. Wire the pulse shaping filter coefficients parameter of the MT Generate Filter Coefficients VI to this parameter. When generating the filter coefficients, ensure that the value of the pulse shaping samples per symbol parameter of the MT Generate Filter Coefficients VI is equal to the value of the samples per symbol element of the CPM system parameters cluster.
|
 |
flush buffers? forces out samples from the input complex waveform that are delayed due to the FIR filters used in the demodulation algorithm. Set this parameter to TRUE during single-shot operations and during the last iteration of continuous operations. The default is FALSE.
 |
Note Setting flush buffers? to TRUE destroys the internal states of the algorithms such that you cannot perform continuous processing on the signal during subsequent iterations. If flush buffers? is set to TRUE, you must set reset? to TRUE on the subsequent iteration. |
|
 |
error in (no error) can accept error information wired from
previously called VIs. Use this information to decide if any functionality
should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the front
panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
 |
status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred or FALSE (checkmark) to
indicate a warning or that no error occurred. Right-click the front panel
error in control and select Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the
error.
|
 |
code identifies the error or warning code. Right-click the front
panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the
error.
|
 |
source describes the origin of the error or warning. Right-click the
front panel error in control and select Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the
error.
|
|
 |
output bit stream returns the demodulated information bit stream.
 |
Note
For CPM systems with more than 1 bit per symbol, such as 4-CPM, the symbols are converted to bits in least significant bit (LSB) first order. For example, if the detected symbols are 2,1,... the generated bits are 0,1,1,0... |
|
 |
sync found index returns the symbol index within the input
complex waveform where the peak correlation to the sync sequence was found. If no sync sequence is specified in the synchronization parameters cluster, this parameter returns
the offset from the start of the input complex
waveform to the first complete symbol.
|
 |
error out passes error or warning information out of a VI to be used by
other VIs. Right-click the front panel error out indicator and select
Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the
error.
 |
status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred or FALSE (checkmark) to
indicate a warning or that no error occurred. Right-click the front panel
error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the
error.
|
 |
code is the error or warning code. Right-click the front panel
error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the
error.
|
 |
source describes the origin of the error or warning. Right-click the
front panel error out indicator and select Explain Error or Explain
Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the
error.
|
|
NI recommends using some form of pulse shaping on continuous-phase
CPM-modulated signals to optimize demodulator performance. Demodulator performance under
these conditions can also be improved by increasing the number of samples per symbol,
but you can achieve better performance by using some form of pulse shaping.