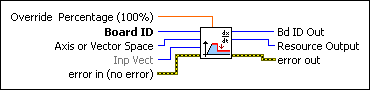
Load Velocity OverrideLoads an instantaneous velocity override for an axis or vector space.
| Device Compatibility
|

|
Override Percentage (100%) is a single precision floating point value from 0 to 150%. This value directly scales the programmed velocity. The default value is 100% (no effect). | ||||||
 |
Board ID is a unique number assigned by Measurement & Automation Explorer (MAX) used to send and receive commands and data to or from a specific NI motion controller. | ||||||
 |
Axis or Vector Space is the axis or vector space to control. | ||||||
 |
Inp Vect indicates the source of the data for this VI. Available input vectors include immediate (0xFF), variable (0x01 through 0x78), or indirect variable (0x81 through 0xF8). Refer to Input and Return Vectors for more detailed information. | ||||||
 |
error in (no error) describes error conditions that occur before this VI runs. The default input of this cluster is no error. If an error already occurred, this VI returns the value of error in in error out. The VI runs normally only if no incoming error exists. Otherwise, the VI passes the error in value to error out. The error in cluster contains the following parameters:
|
||||||
 |
Bd ID Out is provided for flow control. You can string together NI-Motion VIs by wiring the Bd ID Out terminal of one VI to the Board ID terminal of the next VI. | ||||||
 |
Resource Output is the Axis, Vector Space, ADC, or Encoder you wired into the VI. Use Resource Output to pass the resource to another VI and/or to display information about the device. | ||||||
 |
error out contains error information. If error in indicates an error, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI produces.
|
Using This VI
The Load Velocity Override VI scales the operating velocity on an axis or vector space from 0 to 150%. Velocity override is not double-buffered. The VI takes effect immediately and does not require a Start or Blend Motion VI execution to change the operating velocity. All velocity changes use the loaded values of acceleration, deceleration, and s-curve to smoothly transition the velocity to its new value.
Velocity override scales velocity in linear interpolation as well as in circular, helical, and spherical arcs.
 |
Note Velocity override is not valid for contoured moves. |
You can load velocity override to individual axes or to a vector space for coordinated velocity scaling. When sent to a vector space, the velocity override is broadcast to all axes in the vector space to change the per-axis overrides. If you later want to operate an axis independently with a different velocity override, you must execute the Load Velocity Override VI again for that axis. Note that this also works with gearing. In addition to following the position of the master axis, the slave follows the velocity of the master axis.
After it is loaded, velocity override remains in effect until changed by another call to this VI. All subsequent moves are at velocities scaled by the most recent override percentage. At power-up reset, velocity override is always reset to 100%.
Velocity override is commonly used in machine tool and other applications to reduce the speed of a programmed motion sequence and can be used to implement a feed hold by setting the value to zero (0). You can directly use a scaled value from an analog input as the velocity override value.
Remarks
This section includes information about how the behavior of this VI differs among the controllers that support it.
NI 73xx Controller Considerations
The following list includes considerations you must make when you are using this VI with a 73xx motion controller:
- For 73xx controllers, the resolution of this VI is approximately 0.4%.
- The conversion from floating-point to fixed-point is performed on the host computer, not on the motion controller. To load velocity override from an onboard variable, you must use the integer representation of 0 to 384.
- All axes in a vector space must have the same velocity override. If axes have different velocity overrides, the vector move cannot function as expected. This mode is legal and does not generate an error, but it causes the axes to finish their moves at different times.
NI SoftMotion Controller Considerations
The following list includes considerations you must make when you are using this VI with the NI SoftMotion Controller:
- If velocity override is loaded on an axis, it is applied only during single-axis moves.
- If the velocity override is loaded on a vector space, it does not overwrite the values for the axes that are in the vector space. In this case, the velocity override is applied only during vector space moves.
- The range for the Override Percentage is the full 64-bit range, and is not limited to 150% for the NI SoftMotion Controller.