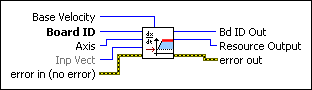
Load Base VelocitySets the base velocity used by the trajectory control loop for the axis specified.
| Device Compatibility
|
 |
Base Velocity is the base velocity for the stepper axis in steps/second and is a 16-bit data word in the range of 0 through 65,535. The default value is 0. | ||||||
 |
Board ID is a unique number assigned by Measurement & Automation Explorer (MAX) used to send and receive commands and data to or from a specific NI motion controller. | ||||||
 |
Axis is the axis to control. | ||||||
 |
Inp Vect indicates the source of the data for this VI. Available input vectors include immediate (0xFF), variable (0x01 through 0x78), or indirect variable (0x81 through 0xF8). Refer to Input and Return Vectors for more detailed information. | ||||||
 |
error in (no error) describes error conditions that occur before this VI runs. The default input of this cluster is no error. If an error already occurred, this VI returns the value of error in in error out. The VI runs normally only if no incoming error exists. Otherwise, the VI passes the error in value to error out. The error in cluster contains the following parameters:
|
||||||
 |
Bd ID Out is provided for flow control. You can string together NI-Motion VIs by wiring the Bd ID Out terminal of one VI to the Board ID terminal of the next VI. | ||||||
 |
Resource Output is the Axis, Vector Space, ADC, or Encoder you wired into the VI. Use Resource Output to pass the resource to another VI and/or to display information about the device. | ||||||
 |
error out contains error information. If error in indicates an error, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI produces.
|
Using This VI
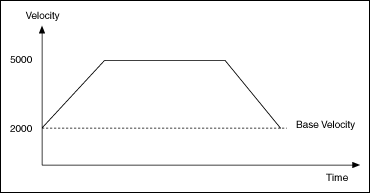
Base velocity is the minimum step rate used by the trajectory generator during acceleration and deceleration. Base velocity is useful when the system uses full-step or half-step mode. Base velocity is not necessary if the system uses microstepping.
If the target velocity loaded with the Load Velocity VI is lower than the base velocity, the base velocity is reduced to equal the loaded target velocity.
 |
Note This VI is valid only on axes configured as steppers, so you must configure an axis as a stepper using the Configure Axis Resources VI before executing this VI. |
Example
If the base velocity loaded is 2,000 steps/s and the loaded velocity is 5000, the axis starts at the base velocity and accelerates to the loaded velocity. The axis then decelerates to the base velocity and stops, as shown in the following figure.