The Log file frame
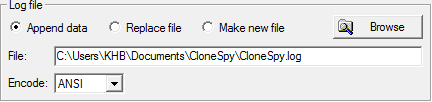
In this frame you can specify the file which CloneSpy will use for logging. The controls in this frame will only be accessible if you enable the logging option in the Logging properties frame.
All data specified in the Logging properties frame will be written into the log file indicated in the edit box at the bottom of the frame. If you want CloneSpy to use a different file to store the data, specify another file by clicking the Browse button, or modify the path in the edit box. In the latter case the entry must fulfill the requirements described in the section Specifying paths.
If the specified log file does not exist, it will be created when the scan is started. If the log file already exists, the three radio buttons at the top of the frame allow for three options:

In this frame you can specify the file which CloneSpy will use for logging. The controls in this frame will only be accessible if you enable the logging option in the Logging properties frame.
All data specified in the Logging properties frame will be written into the log file indicated in the edit box at the bottom of the frame. If you want CloneSpy to use a different file to store the data, specify another file by clicking the Browse button, or modify the path in the edit box. In the latter case the entry must fulfill the requirements described in the section Specifying paths.
If the specified log file does not exist, it will be created when the scan is started. If the log file already exists, the three radio buttons at the top of the frame allow for three options:
- Append data: If you choose this option the information about a scan will be added at the end of the existing log file. Remember that over a period of time quite large files may be generated if you select this option.
- Replace file: If you select this button the existing file will be deleted and a new one created.
- Make new file: This option will force CloneSpy to generate a new log file. The new log file will have the same name as entered in the edit box followed by an underscore character and a number. Assume that the file CloneSpy.log is chosen and that it already exists. In this case the program will try to create a log file which has the name CloneSpy_1.log. If this file also exists, CloneSpy_2.log is tested and so on.