Rotating Knife
The purpose of this application is to cut a web with a rotating knife. The blade must cut precisely between labels on the web. Because the web material can stretch under certain conditions, it is not enough to cut the web at constant length, because the length of each label can vary. To accomplish this task, the web is marked one time per cycle at the required cutting location. The motion controller reads this mark using a sensor and performs the necessary correction.
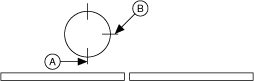
To simplify this example, assume that the length of the cut is equal to the circumference of the knife. Under ideal conditions, the mark should be read when the blade is at position A, as shown in the figure below. Therefore, the motor should move one revolution without any correction before causing the cut.
 |
Tip Refer to Electronic Gearing and Camming for information about superimposed moves/registration applications. |
Solution
The rotary knife is electronically geared to the web with a gear ratio of 1:1, which ensures that at the time of cut, the speed of the web and the knife is the same. The speed of each must be the same to make a clean cut without stretching the web. Also, under ideal conditions, the web and rotating knife move the exact same distance. For example, the length of the cut might be one revolution, which is equal to 2,000 counts.
The sensor reading the mark is connected to one of the high-speed capture lines on the motion controller. Because the elasticity of the web material results in varying label lengths, the mark can be read before the blade is at position A or after it is at position A. The application must correct the position where the blade of the rotary knife should be when the high-speed capture occurs. This correction must occur after the blade has crossed position A so that the current cut is not damaged. To accomplish this goal, mark the correction point to be at position B, as shown in the following figure.
|
|
| A Synchronization Point | B Correction Point |
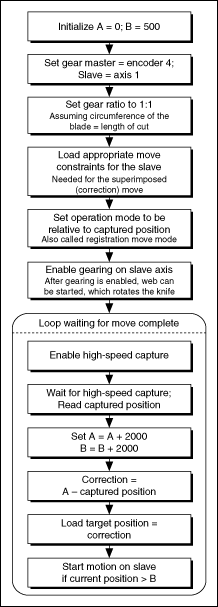
Rotating Knife Algorithm
The following figure shows the basic algorithm for the rotating knife application applicable to both C/C++ and LabVIEW code.