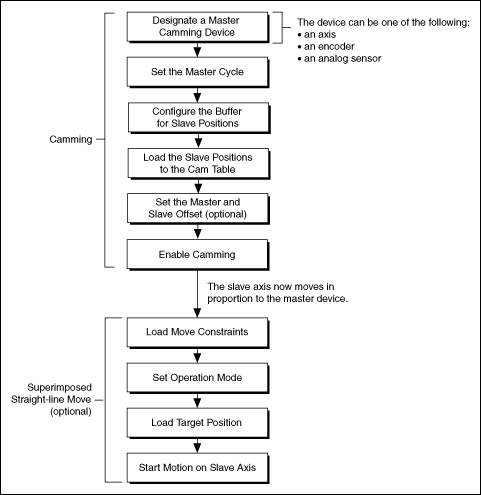
Camming
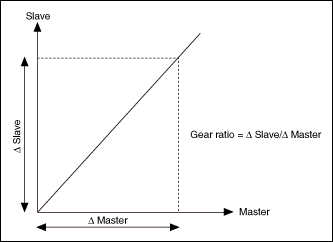
Electronic camming operates similarly to electronic gearing in that the move distance of an axis is proportional to the move distance of its master device. Camming differs from gearing in how the master/slave ratio is handled by the motion controller. Gearing is used in applications where a constant gear value creates a linear slave position profile, as shown.
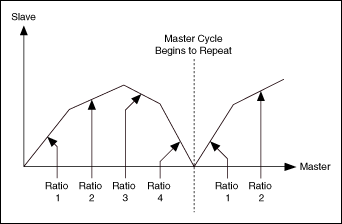
Camming creates a more flexible profile by using more master/slave ratios. These ratios are handled automatically by the motion controller, allowing precise switching of the gear ratios, as shown in the following figure. Camming is used in applications where the slave axis follows a non-linear profile from a master device.
Electronic Camming Algorithm
The following figure shows a generic electronic gearing algorithm applicable to both C/C++ and LabVIEW code. Similar to gearing, in a camming application, a slave axis can perform any move when camming is enabled. The move profile is superimposed over the camming profile.