NI 73xx Velocity in RPM
Velocity values in RPM are converted to an internal 16.16 fixed-point format in units of counts (steps) per sample period (update period) before being used by the trajectory generator. NI-Motion can control velocity to 1/65,536 of a count or step per sample.
The following table shows the minimum and maximum velocity in counts/min. Use the formula shown in the Calculation Based on Units column to determine the counts/min value to RPM.
| Update Rate | MIN | MAX | Calculation Based on Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.5 µs | 14.648438 counts/min | For servo motors, the maximum counts/min is 1.2 billion independent of the update rate. | ±RPMmax = MAX×1/r where r = counts/revolution |
| 125 µs | 7.324219 counts/min | ||
| 187.5 µs | 4.882813 counts/min | ||
| 250 µs | 3.662109 counts/min | ||
| 312.5 µs | 2.929688 counts/min | For stepper motors, the maximum counts/min value is dependent on the controller:
|
±RPMmin = MIN×1/r where r = counts/revolution |
| 375 µs | 2.441406 counts/min | ||
| 437.5 µs | 2.092634 counts/min | ||
| 500 µs | 1.831055 counts/min |
You can calculate this minimum velocity increment in RPM with the following formula:
minimum RPM = Vmin × (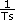 ) × 60 × (
) × 60 × (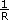 )
)
where
Vmin = 1/65,536 counts/sample or steps/sample
Ts = sample period in seconds per sample
60 = number of seconds in a minute
R = counts or steps per revolution
or
minimum RPM = MIN × 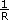
You also can calculate the minimum velocity using the formula shown in the Calculation Based on Units column.
For a typical servo axis with 2,000 counts per revolution operating at a 250 µs update rate, the minimum RPM increment is
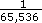 ×
× 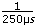 × 60 ×
× 60 × 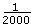 = 0.00183105 RPM
= 0.00183105 RPM
or
3.662109 × 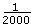 = 0.00183105 RPM
= 0.00183105 RPM
You can calculate the maximum velocity in RPM with the following equation:
maximum RPM = Vmax × 60 × 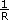
where
Vmax = 20 MHz for servos
8 MHz for steppers on a NI 7350 controller
4 MHz for steppers on a NI 7330, NI 7340, or NI 7390 motion controller
R = counts/steps per revolution
and is constrained by acceleration/deceleration according to the following equation:
velocity  (65,536 × deceleration) acceleration
(65,536 × deceleration) acceleration
where velocity is in counts/sample and acceleration and deceleration are in counts/sample2.
From the example, the maximum RPM is
(20 × 106) × 60 × 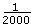 = 600,000 RPM
= 600,000 RPM
RPM values stored in onboard variables are in double-precision IEEE format (f64).