NI 73xx Acceleration in RPS/s
Acceleration and deceleration values in RPS/s are converted to an internal 16.16 fixed-point format in units of counts/sample2 or steps/sample2 before being used by the trajectory generator.
The following table shows the minimum and maximum acceleration update rates in counts/sec2.
| Update Rate | MAX | MIN | Calculation Based on Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.5 µs | 2,048,000,000 counts/sec2 | 3906 counts/sec2 | ±RPS/smax = MAX×1/r where r = counts/revolution |
| 125 µs | 2,048,000,000 counts/sec2 | 977 counts/sec2 | |
| 187.5 µs | 910,222,222 counts/sec2 | 434 counts/sec2 | |
| 250 µs | 512,000,000 counts/sec2 | 244 counts/sec2 | |
| 312.5 µs | 327,680,000 counts/sec2 | 156 counts/sec2 | ±RPS/smin = MIN×1/r where r = counts/revolution |
| 375 µs | 227,555,556 counts/sec2 | 109 counts/sec2 | |
| 437.5 µs | 167,183,673 counts/sec2 | 80 counts/sec2 | |
| 500 µs | 128,000,000 counts/sec2 | 61 counts/sec2 |
You can calculate the minimum acceleration increment in RPS/s with the following formula:
RPS/sec = Amin × (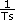 )2 ×
)2 × 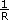
where
Amin = 1/65,536 counts/sample2 or steps/sample2
Ts = sample period in seconds per sample
R = counts or steps per revolution
or
RPM/s = MIN × 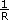
For a typical servo axis with 2,000 counts or steps per revolution operating at the 250 µs update rate, calculate the minimum RPS/s increment using the following equation:
(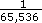 ) × (
) × (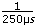 )2 ×
)2 × 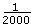 = 0.122070 RPS/s
= 0.122070 RPS/s
or
244 × 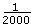 = 0.122
= 0.122
You can calculate the maximum RPS/s using the following equation:
maximum RPS/s = Amax × (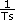 )2 × (
)2 × (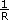 )
)
where
Amax = 32 counts/sample2
Ts = sample period in seconds per sample
R = counts or steps per revolution
and is constrained according to the following equations:
acceleration  256 × deceleration
256 × deceleration
deceleration  65536 × acceleration
65536 × acceleration
or
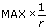
For a typical servo axis with 2,000 counts or steps per revolution operating at the 250 µs update rate, calculate the maximum RPS/s increment using the following equation:
32 × (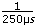 )2 ×
)2 × 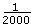 = 256,000 RPS/s
= 256,000 RPS/s
RPS/s values stored in onboard variables are in double-precision IEEE format (f64).