Coordinate Space
With the exception of the arc move, you can execute all basic moves on either a single axis or on a coordinate space. A coordinate space is a logical grouping of axes. If you are performing a move that uses more than one axis, you must specify a coordinate space made up of the axes the move will use, as shown in the following figure.
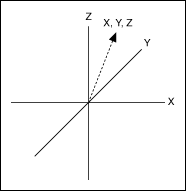
 |
Note Arc moves always execute on a coordinate space. |
Use the Configure Vector Space VI or function to configure a coordinate space. This function creates a logical mapping of axes and treats the axes as part of a coordinate space. The function then executes the move generated by the trajectory generator on the vector, and treats all the move constraints as vector values.
Multi-Starts versus Coordinate Spaces
Coordinate spaces always start and end the motion of all axes simultaneously. You can use multi-starts to create a similar effect without grouping axes into coordinate spaces. Using a multi-start automatically starts all axes virtually simultaneously. To simultaneously end the moves, you must calculate the move constraints to end travel at the same time. In coordinate spaces, these values are calculated automatically.