Several SNMP MIB browsers are available. Users can also install a customized MIB browser specific to their application. This help file describes using the iReasoning MIB browser to run the demo app. The iReasoning MIB browser can be obtained from: 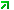 http://www.ireasoning.com/downloadmibbrowserlicense.shtml. The MIB script upload, the MIB tree structure display, and the SNMP query mechanism procedures vary from browser to browser.
http://www.ireasoning.com/downloadmibbrowserlicense.shtml. The MIB script upload, the MIB tree structure display, and the SNMP query mechanism procedures vary from browser to browser.
Note that the use of a MIB browser or other third-party tools may require that users review and agree to the terms of a license. Microchip's reference to the iReasoning MIB browser is for the users' convenience. It is the user's responsibility to obtain information about, and comply with the terms of, any applicable licenses.
Once your browser installation has been completed, perform the following steps:
- Copy the mchip.mib file to the MIB file directory of your browser (e.g. "C:\Program Files\ireasoning\mibbrowser\mibs").
- Open the iReasoning browser, select File->Load MIBs, and select the mchip.mib, RFC1213.mib and SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB.mib (If SNMPv3 server is enabled) file.
The Microchip MIB directory will be displayed in the SNMP MIB pane.
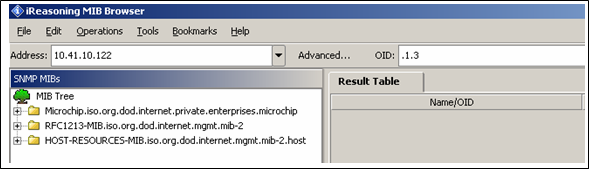
The minimum set of RFC 1213 MIB2 variables that are required to identify the Microchip node as an SNMP node to the network are implemented. These variables can be accessed by any SNMP browser with a "public" type community name. Refer to AN870 - "SNMP V2c Agent for Microchip TCP/IP Stack" for more details on the MIB scripts, community names, and demo SNMP MIB variable tree structure. The following figure shows the variables implemented in the Microchip SNMP Agent.
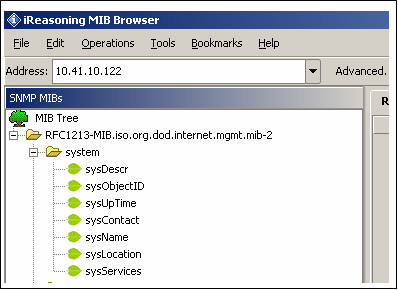
The ASN.1 format mchip.mib file is defined with a private variable tree structure for the MIB variables. Also the mchp.mib is added with number of OIDs which could be accessed only with SNMPv3 request. The browser can access every variable in the MIB database provided the community name matches. The access to the MIB variables is restricted to the type of the request. The RFC1213 mib variables could be accessed with SNMPv2c/v3 request. But the SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB.mib variables could only be accessed with SNMPv3 reqeust if the credentials are matched and the message is authenticated. To modify these MIB variables, corresponding changes must be made to both MIB scripts (snmp.mib and mchip.mib). The following figure shows the Microchip private MIB variable tree structure in the browser.
Configuring the Browser
To configure the iReasoning MIB browser:
- Select the "Advanced" tab in the browser.
The following configuration window will be displayed:
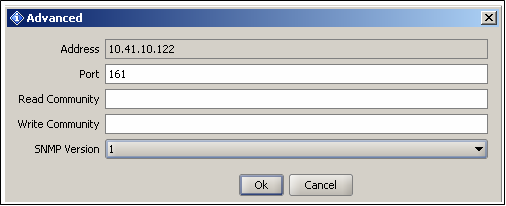
- If V2C services are required, select SNMP version V2c, configure the Read and Write community to the browser.
- The V2c agent will respond only to the queries from SNMP MIB browsers using the same community. That is, the V2c agent and the browser should be members of the same community.
- If the community fields are left blank, the manager sends the SNMP request with the community name as "public."
- The V2c agent is configured by default with 3 Read communities ("public", "read", "") and 3 Write communities ("private","write","public").
- The default maximum community length is 8 characters.
- As the default communities also contain the "public" community name, the agent will respond to all of the browsers requesting the "public" community.
- The TCP/IP Configuration Wizard can be used to configure the default SNMP community names. At run time, the community names can be dynamically configured using the HTTP interface for SNMP community name configuration.
If the V2c agent receives an SNMP request with an unknown community name, the agent will generate an Authentication trap.
The V2c agent's multiple community support feature enables the user application to provide limited access to the requesting browser based on the community name used by the browser to access the MIB database variables of the agent.
- If SNMPv3 services are required, select the SNMP Version as 'V3' in the 'Advanced' tab of the SNMP MIB Browser. The following configuration window will be displayed:
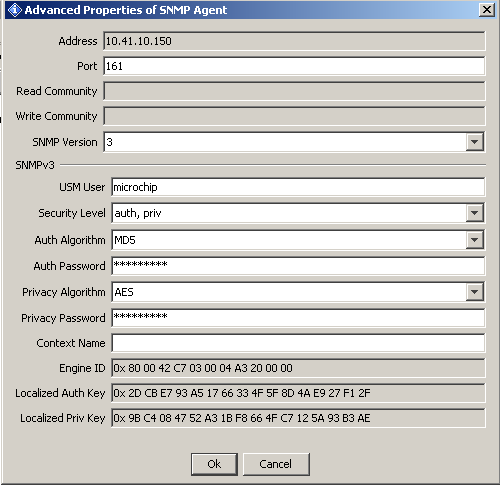
- If SNMPv3 services are required, SNMPv3 browser is required to be configured with the user name, authentication and privacy password, message authentication hash type, privacy protocol type. The SNMP server would respond only if one of the user credentials and user security parameters in the below table is configured at the manager. The below table is stored in the global structure with the SNMPv3 server stack. The SNMPv3 server would only respond if the request credentials of the MIB browser matches to that of the stored user data base of the SNMP server.
|
|
USER 1 |
USER 2 |
USER 3 |
|
USM User |
microchip |
SnmpAdmin |
root |
|
Security Level |
auth, priv |
auth, no priv |
no auth, no priv |
|
Auth Algorithm |
MD5 |
SHA1 |
|
|
Auth password |
auth12345 |
ChandlerUS |
|
|
Privacy Algorithm |
AES |
|
|
|
Privacy password |
priv12345 |
|
|
- The Microchip SNMPv3 stack does support only one Context Engine ID with the server. Leave the "Context Name" option in the "Advanced" tab empty. It is ignored on the server.
- According to the user and the auth and privacy protocols configured with the SNMP browser, the UDP authenticated and encrypted message would be exchanged between server and the client.
- If the USER 1 values, as in above table, are configured in the MIB browser, the data exchange between client and server is encrypted and authenticated. The PDU could be captured in the Ethernet packet sniffer like WireShark and examined. As the data is encrypted and authenticated, the data integrity and the privacy is achieved.
- If USER 2 values, as in above table, are configured in the MIB browser, the data exchange between client and server is authenticated. The data integrity would be checked once the data is received at either end. The message authentication mechanism protects from the possible data sniffing and modification threat, and alos guarantees that the data is received from the authenticated and guaranteed source.
- if USER3 values, as in above table, are configured in the MIB browser, the data exchange between client and server is neither authenticated nor encrypted.
- Considering the above three USER configurations, if the SNMP server is to be accessed over WAN, in the internet cloud, tha data should be encrypted and authenticated to have the highest level of data privacy and integrity.
- Configure the IP address of the SNMP agent to the "Address field.
- Select the variable to be accessed from the agent MIB database from the SNMP MIBs pane. The selected variable's OID can be seen in the OID tab in the following figure.
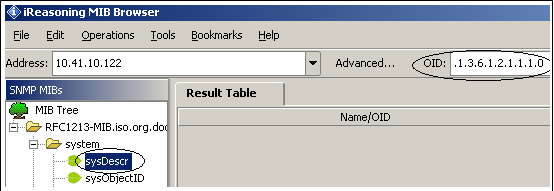
- Select the SNMP Get operation from the operations tab.

- The SNMPv3 server demo MIB is included with RFC1213 SNMPv2 MIB variables, private mib variables and the SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB variables. If the SNMPv2C request with validated community name is generated from the MIB Browser, only set of few variables is accessed. The access to the MIB variables is restricted to the type of SNMP version request received. If the SNMPv3 request with correct credentials is generated from the MIB Browser, the complete MIB access is provided.
- The user would require to decide on which part of the MIB should be required to be restricted depending upon the SNMP version type. The MIB design is the one of the important step in deciding the MIB tree structure and the variable to be placed accordingly.
- The SNMP server demo MIB is added with a static variable OID named as "snmpv3PvtObject" with OID value as 43.6.1.4.1.17095.6.1. This variable is placed in the private branch of the MIB by creating an independent branch. All the other variables in the private branch are accessible by SNMPv2c request. The access to this static variable is restricted by the SNMP version type. Only the SNMPv3 request with correct credentials could access this variable.
Exploring the Demo
After the MIB script is uploaded to the SNMP browser, the MIB tree structure will be displayed in the browser. Any of the variables in this tree can be accessed (using SNMP operations) from the agent if the agent supports these variables. The browser and agent should be members of the same community. To learn more about SNMP operations, PDU types, and terminology, refer to AN870 - "SNMP V2C Agent for Microchip TCP/IP Stack."