Spacecraft Epoch
Spacecraft Epoch — The spacecraft epoch
Description
The epoch of a Spacecraft is the time and date corresponding to the specified orbit state. See the Spacecraft Orbit State section for interactions between the epoch, coordinate system, and spacecraft state fields.
See Also: Spacecraft
Caution
GMAT’s Modified Julian Date (MJD) format differs from that of other software. The Modified Julian format is a constant offset from the full Julian date (JD):
GMAT uses a non-standard offset, as shown in the following table.
| Epoch Type | GMAT | common |
| reference epoch | 05 Jan 1941 12:00:00.000 | 17 Nov 1858 00:00:00.000 |
| Modified Julian offset | 2430000.0 | 2400000.5 |
Fields
| Field | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DateFormat |
The time system and format of the Epoch field. In the GUI, this field is called EpochFormat.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch |
The time and date corresponding to the specified orbit state.
|
||||||||||||
| A1ModJulian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the A.1 system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.A1ModJulian | The spacecraft orbit epoch in the A.1 system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| CurrA1MJD |
This field has been deprecated and should no longer be used. The current epoch in the A1ModJulian format. This field can only be used within the mission sequence.
|
||||||||||||
| A1Gregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the A.1 system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| TAIGregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TAI system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| TAIModJulian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TAI system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| TDBGregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TDB system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| TDBModJulian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TDB system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| TTGregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TT system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| TTModJulian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TT system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| UTCGregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the UTC system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| UTCModJulian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the UTC system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.A1Gregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the A.1 system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.TAIGregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TAI system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.TAIModJulian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TAI system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.TDBGregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TDB system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.TDBModJulian | The Spacecraftorbit epoch in the TDB system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.TTGregorian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the TT system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.TTModJulian | The Spacecraftorbit epoch in the TT system and the Modified Julian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.UTCGregorian | The Spacecraftorbit epoch in the UTC system and the Gregorian format.
|
||||||||||||
| Epoch.UTCModJulian | The Spacecraft orbit epoch in the UTC system and the Modified Julian format.
|
GUI
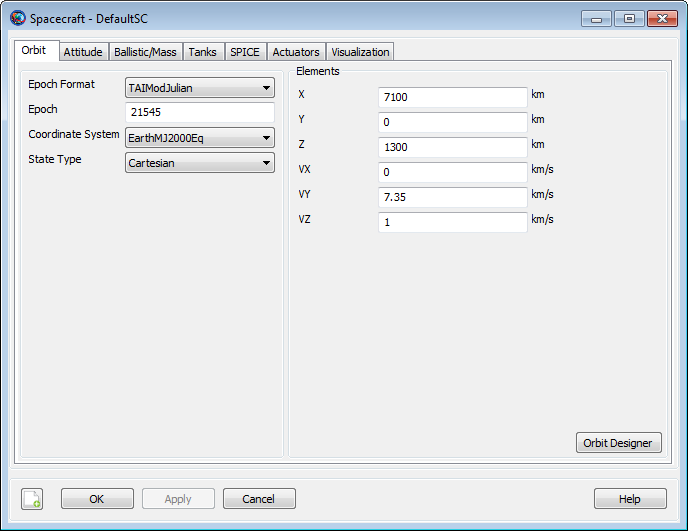
|
A change in EpochFormat causes an immediate update to Epoch to reflect the chosen time system and format.
Remarks
GMAT supports five time systems or scales and two formats:
| A.1 | USNO atomic time; GMAT’s internal time system |
| TAI | International Atomic Time |
| TDB | Barycentric Dynamical Time |
| TT | Terrestrial Time |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time |
| Gregorian |
Text with the following format:
|
||||||||||||||
| Modified Julian | Floating-point number of days from a reference epoch. In GMAT, the reference epoch is 05 Jan 1941 12:00:00.000 (JD 2430000.0). |
The epoch can be set in multiple ways. The default method is to set the DateFormat field to the desired time system and format, then set the Epoch field to the desired epoch. This method cannot be used to get the epoch value, such as on the right-hand side of an assignment statement.
aSat.DateFormat = UTCGregorian
aSat.Epoch = '18 May 2012 12:00:00.000'
An alternate method is to specify the DateFormat in the parameter name. This method works in both “get” and “set” modes.
aSat.Epoch.UTCGregorian = '18 May 2012 12:00:00.000'
Report aReport aSat.Epoch.UTCGregorian
A third method can be used in “get” mode everywhere, but in “set” mode only in the mission sequence (i.e. after the BeginMissionSequence command).
aSat.UTCGregorian = '18 May 2012 12:00:00.000'
Report aReport aSat.UTCGregorian
GMAT uses the A.1 time system in the Modified Julian format for its internal calculations. The system converts all other systems and formats on input and again at output.
Leap Seconds
When converting to and from the UTC time system, GMAT includes
leap seconds as appropriate, according to the
tai-utc.dat data file from the IERS. This file
contains the conversion between TAI and UTC, including all leap seconds
that have been added or announced.
GMAT applies the leap second as the last second before the date
listed in the tai-utc.dat file, which historically
has been either January 1 or July 1. In the Gregorian date format, the
leap second appears as a “60th second”: for
example, “31 Dec 2008 23:59:60.000”. From the International Astronomical
Union's Standards of Fundamental Astronomy "SOFA Time Scale and Calendar
Tools" documentation: "Note that UTC has to be expressed as
hours, minutes and seconds (or at least in seconds in a given day) if
leap seconds are to be taken into account in the correct
manner. In particular, it is inappropriate to express UTC as
a Julian Date, because there will be an ambiguity during a leap second
so that for example 1994 June 30 23:59:60:0 and 1994 July 1 00:00:00:0
would both come out as MJD 49534.00000 and because subtracting two such
JDs would not yield the correct interval in cases that contain leap
seconds." For this reason, we discourage use of the UTC modified Julian
system, and recommend using UTC Gregorian when a UTC time system is
required.
For epochs prior to the first entry in the leap-second file, the UTC and TAI time systems are considered identical (i.e. zero leap seconds are added). For epochs after the last entry, the leap second count from the last entry is used.
The tai-utc.dat file is periodically updated
by the IERS when new leap seconds are announced. The latest version of
this file can always be found at http://maia.usno.navy.mil/ser7/tai-utc.dat.
To replace it, download the latest version and replace GMAT’s file in
the location
<GMAT>/data/time/tai-utc.dat,
where <GMAT> is
the install directory of GMAT on your system.
Examples
Setting the epoch for propagation
Create Spacecraft aSat
aSat.DateFormat = TAIModJulian
aSat.Epoch = 25562.5
Create ForceModel aFM
Create Propagator aProp
aProp.FM = aFM
BeginMissionSequence
Propagate aProp(aSat) {aSat.ElapsedDays = 1}
Plotting and reporting the epoch (syntax #1)
Create Spacecraft aSat
aSat.DateFormat = A1Gregorian
aSat.Epoch = '12 Jul 2015 08:21:45.921'
Create XYPlot aPlot
aPlot.XVariable = aSat.UTCModJulian
aPlot.YVariables = aSat.Earth.Altitude
Create Report aReport
aReport.Add = {aSat.UTCGregorian, aSat.EarthMJ2000Eq.ECC}
Plotting and reporting the epoch (syntax #2)
Create Spacecraft aSat
aSat.DateFormat = TTGregorian
aSat.Epoch = '01 Dec 1978 00:00:00.000'
Create XYPlot aPlot
aPlot.XVariable = aSat.Epoch.TTModJulian
aPlot.YVariables = aSat.Earth.RMAG
Create Report aReport
aReport.Add = {aSat.Epoch.A1Gregorian, aSat.Earth.RMAG}