Below we discuss the files and data that are distributed with GMAT and are required for GMAT execution. GMAT uses many types of data files, including planetary ephemeris files, Earth orientation data, leap second files, and gravity coefficient files. This section describes how these files are organized and the controls provided to customize them.
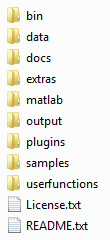
The default directory structure for GMAT is broken into eight main
subdirectories, as shown in Figure 4.1, “GMAT Root Directory Structure”.
These directories organize the files and data used to run GMAT, including
binary libraries, data files, texture maps, and 3D models. The only two
files in the GMAT root directory are license.txt,
which contains the text of the Apache License 2.0, and
README.txt, which contains user information for the
current GMAT release. A summary of the contents of each subdirectory is
provided in the sections below.
The bin directory contains all binary files
required for the core functionality of GMAT. These libraries include the
executable file (GMAT.exe on Windows,
GMAT.app on the Mac, and GMAT
on Linux) and platform-specific support libraries. The
bin directory also contains two text files:
gmat_startup_file.txt and
gmat.ini. The startup file is discussed in detail
in a separate section below. The gmat.ini file is
used to configure some GUI panels, set paths to external web links, and
define GUI tooltip messages.
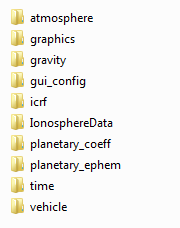
The data directory contains all required data
files to run GMAT and is organized according to data type, as shown in
Figure 4.2, “GMAT Data Directory Structure” and described below.
The graphics directory contains data files
for GMAT’s visualization utilities, as well as application icons and
images. The splash directory contains the GMAT
splash screen that is displayed briefly while GMAT is initializing. The
stars directory contains a star catalogue used for
displaying stars in 3D graphics. The texture folder contains texture
maps used for the 2D and 3D graphics resources. The
icons directory contains graphics files for icons
and images loaded at run time, such as the GMAT logo and GUI
icons.
The gravity directory contains gravity
coefficient files for each body with a default non-spherical gravity
model. Within each directory, the coefficient files are named according
to the model they represent, and use the extension
.cof.
The gui_config directory contains files for
configuring some of the GUI dialog boxes for GMAT resources and
commands. These files allow you to easily create a GUI panel for a
user-provided plugin, and are also used by some of the built-in GUI
panels.
The planetary_coeff directory contains the
Earth orientation parameters (EOP) provided by the International Earth
Rotation Service (IERS) and nutation coefficients for different nutation
theories.
The planetary_ephem directory contains
planetary ephemeris data in both DE and SPK formats. The
de directory contains the binary digital ephemeris
DE405 files for the 8 planets, the Moon, and Pluto developed and
distributed by JPL. The spk directory contains the
DE421 SPICE kernel and kernels for selected comets, asteroids and moons.
All ephemeris files distributed with GMAT are in the little-endian
format.
The time directory contains the JPL leap
second kernel naif0010.tls and the GMAT leap second
file tai-utc.dat.
The vehicle directory contains ephemeris data
and 3D models for selected spacecraft. The ephem
directory contains SPK ephemeris files, including orbit, attitude,
frame, and time kernels. The models directory
contains 3D model files in 3DS or POV format for use by GMAT’s
OrbitView visualization resource.
The docs directory contains end-user
documentation, including draft PDF versions of the Mathematical
Specification, Architectural Specification, and Estimation
Specification. The GMAT User’s Guide is available in the
help directory in PDF and HTML formats, and as a
Windows HTML Help file.
The extras directory contains various extra
convenience files that are helpful for working with GMAT but aren't part
of the core codebase. The only file here so far is a syntax coloring
file for the GMAT scripting language in the Notepad++ text
editor.
The matlab directory contains M-files
required for GMAT’s MATLAB interfaces, including the interface to the
fmincon optimizer. All files in the matlab
directory and its subdirectories must be included in your MATLAB path
for the MATLAB interfaces to function properly.
The output directory is the default location
for file output such as ephemeris files and report files. If no path
information is provided for reports or ephemeris files created during a
GMAT session, then those files will be written to the output
folder.
The plugins directory contains optional
plugins that are not required for use of GMAT. The
proprietary directory is used for for third-party
libraries that cannot be distributed freely and is an empty folder in
the open source distribution.
The samples directory contains sample
missions and scripts, ranging from a Hohmann transfer to libration point
station-keeping to Mars B-plane targeting. Example files begin with
"Ex_" and files that correspond to GMAT tutorials begin with "Tut_".
These files are intended to demonstrate GMAT’s capabilities and to
provide you with a potential starting point for building common mission
types for your application and flight regime. Samples with specific
requirements are located in subdirectories such as
NeedMatlab and
NeedVF13ad.
The userfunctions directory contains MATLAB,
Python, and GMAT functions that are included in the GMAT distribution.
You can also store your own custom functions in the subdirectories named
GMAT, Python, and MATLAB. GMAT includes those subdirectories in its
search path to locate functions referenced in GMAT scripts and GMAT
functions.
GMAT uses many emprical data files that are periodically updated. In
some cases files are updated by the owning organization as often as every
3 hours. GMAT is distributed with a python script
\utilities\python\GMATDataFileManager.py that automates
file updates, logs changes, and optionally archives old versions of data
files used by GMAT. See the help documentation contained in the Python
class for detailed usage instructions. Below we describe the emprical data
files used by GMAT, and which startup file variables are used to define
those files' locations on your system. The source of the data file and
comments describe where the files are obtained and how they are
used.
| Startup File Variable | Data Source | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| EOP_FILE | ftp://hpiers.obspm.fr/iers/series/ opa/eopc04_IAU2000/ | The EOP file used by GMAT’s astrodynamics routines. |
| EOP_FILE_SPICE | https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/naif/ generic_kernels/pck/ earth_latest_high_prec.bpc | The EOP file used by SPICE’s astrodynamics routines. |
| PLANETARY_PCK _FILE | https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/naif/ generic_kernels/pck/ | The SPICE planetary constants kernel containing orientation, size and shape data. As of release R2017a, the version is pck00010.pck. This can change and the file checks for new versions. |
| LEAP_SECS_FILE | ftp://maia.usno.navy.mil/ser7/tai-utc.dat | The leap second file used by GMAT’s astrodynamics routines. |
| LSK_FILE | https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/naif/generic_kernels/lsk/ | The leap second file used by SPICE's astrodynamics routines. As of release R2017a, the version is naif0012.tls. This can change and the file checks for new versions. |
| CSSI_FLUX_FILE | ftp://ftp.agi.com/pub/DynamicEarthData/SpaceWeather-All-v1.2.txt | The CSSI Space Weather File used for flux and geomagnetic indeces in drag modelling when a propgator is configured to use the CSSI file as the source for space weather modelling. |
| SCHATTEN_FILE | https://fdf.gsfc.nasa.gov/forms | Requires an account. Cannot be downloaded automatically. |
| IRI2007_APDATA | Constructed from CSSI_FLUX_FILE using GMATDataManager.py | Geomagnetic indices used in the IRI2007 model. |
| EARTH_PCK _PREDICTED_FILE | https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/naif/generic_kernels/pck/ | The SPICE kernel containing predicted, precession, nutation ,nutation corrections, UT1-TAI , and polar motion for the Earth. Used in SPICE's astrodynamic routines. |
| EARTH_PCK _CURRENT_FILE | https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/naif/generic_kernels/pck/ | The SPICE kernel containing historical, precession, nutation ,nutation corrections, UT1-TAI , and polar motion for the Earth. Used in SPICE's astrodynamic routines. |
| LUNA_PCK _CURRENT_FILE | https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/naif/generic_kernels/pck/ | Kernel providing orientation of Lunar Principal Axis (PA) reference frame. Used in SPICE's astrodynamic routines. |
| LUNA_FRAME _KERNEL_FILE | https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/naif/generic_kernels/fk/satellites/ | This frame kernel contains the latest specifications of lunar reference frames realizing the Lunar Principal Axis (PA) and Mean Earth/Polar Axis (ME) reference systems. Used in SPICE's astrodynamic routines. |
Custom plugins are loaded by adding a line to the startup file
(bin/gmat_startup_file.txt) specifying the name and
location of the plugin file. In order for a plugin to work with GMAT,
the plugin library must be placed in the folder referenced in the
startup file. For all details, see the Startup File
reference.
GMAT contains an interface to MATLAB. See the MATLAB Interface reference to configure the MATLAB interface.
GMAT contains an interface to Python. See the Python Interface reference to configure the Python interface.
If you create custom MATLAB functions, you can provide the path to
those files and GMAT will locate them at run time. The default startup
file is configured so you can place MATLAB functions (with a
.m extension) in the
userfunctions/matlab directory. GMAT automatically
searches that location at run time. You can change the location of the
search path to your MATLAB functions by changing these lines in your
startup file to reflect the location of your files with respect to the
GMAT bin folder:
MATLAB_FUNCTION_PATH = ../userfunctions/matlab
If you wish to organize your custom functions in multiple folders, you can add multiple search paths to the startup file. For example,
MATLAB_FUNCTION_PATH = ../MyFunctions/utils MATLAB_FUNCTION_PATH = ../MyFunctions/StateConversion MATLAB_FUNCTION_PATH = ../MyFunctions/TimeConversion
GMAT will search the paths in the order specified in the startup file and will use the first function with a matching name.