NonlinearConstraint
NonlinearConstraint — Specify a constraint used during optimization
Script Syntax
NonlinearConstraintOptimizerName({logical expression})
Description
The NonlinearConstraint command is used within an Optimize/EndOptimize optimization sequence to apply a linear or nonlinear constraint.
Options
| Option | Description | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHS | Allows you to select any single element user defined parameter, except a number, to define the constraint variable. The constraint function is of the form LHS Operator RHS
|
||||||||||
| Operator | logical operator used to specify the constraint function. The constraint function is of the form LHS Operator RHS
|
||||||||||
| OptimizerName | Specifies the solver/optimizer object used to apply a constraint.
|
||||||||||
| RHS | Allows you to select any single element user defined parameter, including a number, to specify the desired value of the constraint variable. The constraint function is of the form LHS Operator RHS
|
GUI
You use a NonlinearConstraint command, within an Optimize/EndOptimize sequence as shown below, to define an equality or inequality constraint that you want to be satisfied at the end of the optimization process.
|
Double click on NonlinearConstraint1 to bring up the NonlinearConstraint command dialog box, shown below.
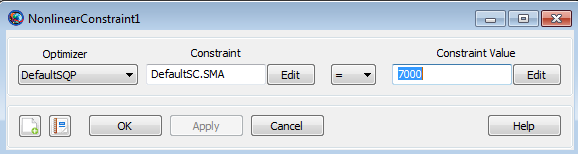
|
You must provide four inputs for the NonlinearConstraint command dialog box above:
-
Choice of Optimizer.
-
Constraint Object. Click the Edit button to the right of this field to select the type of constraint object from three possible choices, Spacecraft, Variable, or Array.
-
Logical operator. Select one from three choices, =, <=, or >=.
-
Constraint Value.
Note that Inputs 2-4 define a logical expression. In the example
above, we have: DefaultSC.SMA = 7000
Remarks
Number of Vary, NonlinearConstraint, and Minimize Commands Within an Optimization Sequence
An Optimization sequence must contain one or more Vary commands. Vary commands must occur before any Minimize or NonlinearConstraint commands.
Multiple NonlinearConstraint commands are allowed. There is exactly one NonlinearConstraint command for every constraint.
It is possible for an Optimize/EndOptimize optimization sequence to contain no NonlinearConstraint commands. In this case, since every optimization sequence must contain (a) one or more NonlinearConstraint commands and/or (b) a single Minimize command, the optimization sequence must contain a single Minimize command.
Command Interactions
The Minimize command is only used within an Optimize/EndOptimize Optimization sequence. See the Optimize command documentation for a complete worked example using the NonlinearConstraint command.
| Optimize command |
NonlinearConstraint commands can only occur within an Optimize/EndOptimize command sequence. |
| Vary command |
Every Optimization sequence must contain at least one Vary command. Vary commands are used to define the control variables associated with an Optimization sequence. |
| Minimize command |
A Minimize command is used within an Optimization sequence to define the objective function that will be minimized. Note that an optimization sequence is allowed to contain, at most, one Minimize command. (An Optimization sequence is not required to contain a Minimize command) |
Examples
% Constrain SMA of Sat to be 7000 km, using SQP1
NonlinearConstraint SQP1( Sat.SMA = 7000 )
% Constrain SMA of Sat to be less than or equal to 7000 km,
% using SQP1
NonlinearConstraint SQP1( Sat.SMA <= 7000 )
% Constrain the SMA of Sat to be greater than or equal to 7000 km,
% using VF13ad1
NonlinearConstraint VF13ad1( Sat.SMA >= 7000 ) As mentioned above, the NonlinearConstraint command only occurs within an Optimize sequence. See the Optimize command help for complete examples showing the use of the NonlinearConstraint command.