Choosing a Stimulus Signal (System Identification Toolkit)
The choice of stimulus signals has an important role in the system behavior and the accuracy of the estimated model. These signals determine the operating points of the system. While the system under test often limits the choice of signals, the input signal must exhibit certain characteristics. These characteristics must produce a response that provides the information you need for developing an accurate model. The following list summarizes these characteristics.
- To obtain meaningful dynamic behavior, you must test the system under conditions similar to the actual operating conditions. When you complete experiments in these conditions, you identify the system in the same conditions under which you will implement the resulting model. This criterion is extremely important for nonlinear systems.
- You want the inputs to the system under test to excite the system. Exciting the system is dependent on the spectrum of the input signal. Specifically, you must excite the system with an input frequency similar to the frequency at which such inputs change during normal operations.
- You want the amplitude of the step input to cover a wide range of variations. Therefore, in the data you use for model estimation, you must cover the normal operation range of system inputs, especially when you use the calculated model for model-based control. To cover the normal operation range, you can combine the positive and negative step changes of different magnitudes in the system inputs.
- You want the input signal to deliver as much input power to the system as possible. However, in the real-world, you must ensure that this input power stays within the limits of the physical system. The crest factor Cf, defined by the following equation, describes this property.
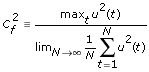
The smaller the crest factor, the better the signal excitation. A better signal excitation results in larger total energy delivery and enhanced signal-to-noise ratio. The theoretical lower bound for the crest factor is 1.
Common Stimulus Signal Types
The system response data is dependent on the physics of the system you want to study. Some systems tend to respond faster than others. Other systems have large time constants and delays. For these reasons, defining a stimulus signal that provides enough excitation to the system is important. The system response must capture the important features of the system dynamics.
You can use the following types of stimulus signals for exciting the system under test.