Analysis > Event Detection & Analysis > Detecting Events
To detect events:
1. Select the Detect Events page in the Event Detection & Analysis window.
2. Select the signal channel to be scanned for events from the Detection Channel list which displays the available analogue and fluorescence channels
Analogue channels:
Select the channel to be scanned from the list. 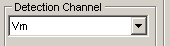
Fluorescence channels:
Select the region of interest to be used from the ROI list (and optionally a background subtraction ROI from the – list). If more than one excitation wavelength is available, select the excitation wavelength channel from the Excit. Ch. list.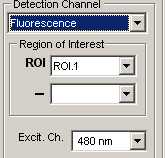
Fluorescence ratios:
Select the region of interest to be used from the ROI list (and optionally a background subtraction ROI from the – list). Select the pair of excitation wavelength channels to be ratioed from the Exc. Ch. Ratio lists.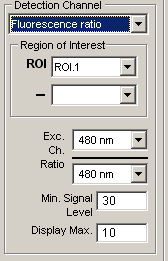
3. Set the upper limit of the ratio display range in the Display Max. box. Enter the minimum signal level that each fluorescence signal channel must exceed to be included in the ratio into the Min. Signal Level box. The ratio is set to zero if either signal within the ratio falls below this level.
4. Enter the event detection criteria.
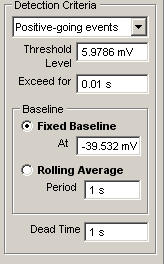
Polarity: Set the polarity of the signals to be detected, selecting Positive-going events for signals which rise to a positive peak relative to the detection baseline, Negative-going events for signals which rise to a negative peak. Select Positive or Negative for to detect both positive- and negative-going signals.
Threshold: Set the signal baseline and detection threshold levels using the horizontal Baseline and Threshold display cursors.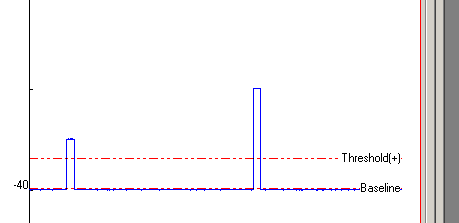
Scroll through the displayed detection channel signal to locate and display the smallest signal to be detected. Place the Baseline cursor on the signal baseline before the event. Place the Threshold cursor at a level which is crossed by the signal and which exceeds the signal background noise. (Note, a pair of (+) and (-) thresholds are displayed when the Positive or Negative detection option is selected.)
Exceed For: Enter the period of time that the signal has to remain above the threshold before detection takes place into the Exceed For box.
Baseline: Select the Fixed Baseline option to maintain the baseline and thresholds at a fixed level throughout the event detection scan. Select the Rolling Average option to make the baseline follow changes in the signal baseline level averaged over the period of time set by the Period box
Dead Time: Enter the period of time after detection of an event before another event can be detected into the Dead Time box. (To avoid detecting an event more than once, the dead time value should be longer than the duration of the event being detected but shorter than the time interval between events.)
5. Click the Detect Events button to detect events within the data file using these criteria.