ncReadObjMult.vi
Purpose
Read multiple frames from a CAN Object.
Format
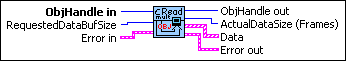
Input
 | ObjHandle in is the object handle from the previous NI-CAN VI. The handle originates from the ncOpen VI. | ||||||
 | RequestedDataBufSize specifies the maximum number of frames desired. For most applications, this will be the same as the configured Read Queue Length in order to empty the read queue with each call to ncReadObjMult. | ||||||
 | Error in describes error conditions occurring before the VI executes. If an error has already occurred, the VI returns the value of the Error in cluster in Error out.
|
Output
 | ObjHandle out is the object handle for the next NI-CAN VI. | ||||||
 | ActualDataSize (Frames) specifies the number of frames returned in Data. This number is less than or equal to RequestedDataBufSize. | ||||||
 | Data returns an array of clusters. Each cluster in the array uses the typedef CanDataTimed.ctl with the following elements:
| ||||||
 | Error out describes error conditions. If the Error in cluster indicated an error, the Error out cluster contains the same information. Otherwise, Error out describes the error status of this VI.
|
Description
Since NI-CAN handles the read queue in the background, this VI does not wait for new frames to arrive. To ensure that new frames are available before calling ncReadObjMult, first wait for the Read Available state or Read Multiple state using ncWaitForState.vi.
When you call ncReadObjMult for an empty read queue (Read Available state false), Error out returns success (status=F, code=0), and ActualDataSize (Frames) returns 0.
When a frame arrives for a full read queue, NI-CAN discards the new frame, and the next call to ncReadObjMult returns the error CanErrOverflowRead (status=T, code= BFF62028 hex). If you detect this overflow, try to read in a relatively tight loop (few milliseconds each read).
You can use the Network Interface and CAN Objects simultaneously. When a CAN frame arrives from the network, NI-CAN first checks the ArbitrationId for an open CAN Object. If no CAN Object applies, NI-CAN checks the comparators and masks of the Network Interface (including the Series 2 Filter Mode attributes). If the frame passes that filter, NI-CAN places the frame into the read queue of the Network Interface.