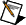ncConfigCANNetRTSI.vi
Purpose
Configure a CAN Network Interface Object with RTSI features.
Format
Input
 | ObjName is the name of the CAN Network Interface Object to configure. This name uses the syntax "CANx", where x is a decimal number starting at zero that indicates the CAN network interface (CAN0, CAN1, up to CAN63). CAN network interface names are associated with physical CAN ports using the Measurement & Automation Explorer (MAX).
The 847x and 847x with Sync series CAN and LIN interfaces do not support ncConfigCANNetRTSI.vi. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | CAN Network Interface Config provides the core configuration attributes of the CAN Network Interface Object. This cluster uses the typedef ncNetAttr.ctl. You can wire in the cluster by first placing it on the front panel from the NI-CAN Controls palette, or you can right-click the VI input and select Create Constant or Create Control. (For more information, refer to ncConfigCANNet.vi.) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | CAN RTSI Config provides RTSI configuration attributes for the CAN Network Interface Object. This cluster uses the typedef ncCANRtsiAttr.ctl. You can wire in the cluster by first placing it on the front panel from the NI-CAN Controls palette, or you can right-click the VI input and select Create Constant or Create Control.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Error in describes error conditions occurring before the VI executes. If an error has already occurred, the VI returns the value of the Error in cluster in Error out.
|
Output
 | Error out describes error conditions. If the Error in cluster indicated an error, the Error out cluster contains the same information. Otherwise, Error out describes the error status of this VI.
|
Description
RTSI is a bus that interconnects National Instruments DAQ, IMAQ, Motion, and CAN boards. This feature allows synchronization of DAQ, IMAQ, Motion, and CAN boards by allowing exchange of timing signals. Using RTSI, a device (board) can control one or more slave devices.
If you are not using RTSI features to synchronize the Network Interface with other National Instruments cards, refer to the ncConfigCANNet VI.
The 847x and 847x with Sync series LIN interfaces do not support ncConfigCANNetRTSI.vi.