LIN Interface Accesses Single Publishing Slave Device
The following steps demonstrate how to use the Frame API functions in a LIN application in which the LIN interface is to provide simple access to a single slave device that publishes data. The steps are shown in the following flowchart.
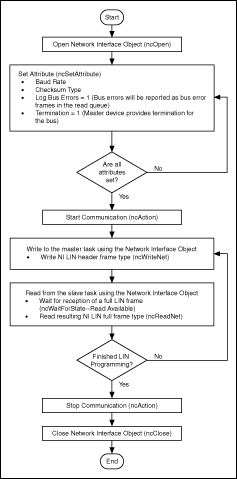
Frame API LIN interface provides simple access to a single slave device that publishes data
- Open a Network Interface Object.
You must call the ncOpenObject function to open the Network Interface Object used in this example.
The ncOpenObject function returns a handle for use in all subsequent Frame API calls for that object. When you are using the LabVIEW function library, this handle is passed through the upper left and right terminals of each Frame API function used after the open.
- Set attributes for the Network Interface Object.
Prior to starting the Network Interface Object, you must configure it with its initial attribute settings. These are configured by calling the ncSetAttribute function with each desired attribute ID and value. This function takes the name of the object to configure, along with the attribute ID and value.
For this example, the baud rate and checksum type should be configured to match those of the slave device. Logging of bus errors is useful for troubleshooting, in the event the device does not behave as expected.
- Start Communication.
You must start communication on the LIN bus before you can use the Network Interface Object to transfer data.
- Write to the master task using the Network Interface Object.
Writing a header frame type containing the ID of the slave device to the LIN interface causes a break-sync-id sequence to be transmitted on the LIN.
- Read from the slave task using the Network Interface Object.
If the slave device is working as expected, it will publish data in response to the header transmitted in step 4. The NI LIN interface slave task will subscribe to this data by default and consequently log it and the header as a full frame type in the read queue. If the slave device is not working as expected, the resulting bus error frame will be placed into the read queue, since logging of bus errors has been enabled. The loading of the full or bus error frame into the read queue will set a read available flag in the interface. ncWaitForState should be used to wait for read available before executing the ncRead or ncReadMult function. Steps 4 and 5 should be repeated for each data set you want to read from the slave device.
- Stop communication.
Stop communication on the LIN bus before closing the Network Interface Object.
- Close the Network Interface Object.