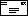
ms:type-local-name([node-set]) Function
Returns the nonqualified name of the XSD type of the current node or the first node (in document order) in the provided node-set.
string ms:type-local-name([node-set])
Remarks
For simple types, the type-local-name function returns a name such as "ID" or "ENTITY". For complex XSD types that have the name attribute specified, the type-local-name returns a nonqualified name such as "Class". Nameless types cause the function to return an empty string.
The following sample expression selects all nodes with the XSD built-in primitive data type "string".
"//*[ms:type-local-name()='string')]"
Example
The following example uses an XSLT template rule to select all the elements inbooks.xml, and to output the elements' data types as defined in books.xsd.
XML File (books.xml)
Use books.xml.
XSD File (books.xsd)
Use books.xsd.
XSLT File (books.xslt)
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:ms="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:xslt"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output method="html"
omit-xml-declaration="yes"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<H3>nodes of all data types:</H3>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="*">
<DIV>
<xsl:value-of select="name()"/> is of
<xsl:value-of select="ms:type-local-name()"/>
</DIV>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>HTML File (books.html)
The HTML file contains a JScript that handles loading XML, XSLT, and XSD files.
<html>
<head>
<script>
function init() {
try {
var objxsd = new ActiveXObject("Msxml2.XMLSchemaCache.5.0");
var objxml = new ActiveXObject("Msxml2.DOMDocument.5.0");
var objxsl = new ActiveXObject("Msxml2.DOMDocument.5.0");
// namespace uri ("urn:books") must be declared as one of the
// namespace delarations in the "books.xml" that is an instance
// of "books.xsd"
objxsd.add("urn:books", "books.xsd");
objxml.schemas = objxsd;
objxml.setProperty("SelectionLanguage", "XPath");
objxml.setProperty("SelectionNamespaces",
"xmlns:ms='urn:schemas-microsoft-com:xslt'");
objxml.async=false;
objxml.validateOnParse=true;
objxml.load("books.xml");
objxsl.async=false;
objxsl.load("books.xsl");
result += "<h2>Used in an XSLT</h2>";
result += objxml.transformNode(objxsl);
document.body.innerHTML = result;
}
catch (e) {
alert(e.description);
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="init()">
</body>
</html>
Output
x:catalog is of book is of author is of string title is of string genre is of string price is of float publish_date is of date description is of string
Notice that x:catalog and book elements have nameless types.
See Also
Using XPath Extension Functions for XSD Support | Data Types in Schemas | XML Schema Reference (XSD) | XML Data Types Reference