KURT
Returns the kurtosis of a data set. Kurtosis characterizes the relative peakedness or flatness of a distribution compared with the normal distribution. Positive kurtosis indicates a relatively peaked distribution. Negative kurtosis indicates a relatively flat distribution.
Syntax
KURT(number1,number2, ...)
Number1,number2, ... are 1 to 30 arguments for which you want to calculate kurtosis.
Remarks
- The arguments must be either numbers or column references that contain numbers.
- If a column reference argument contains text, logical values, or is empty, those values are ignored; however, arguments with the value zero are included.
- If there are fewer than four data points, or if the standard deviation of the sample equals zero, KURT returns the #DIV/0! error value.
- Kurtosis is defined as:
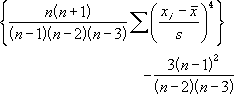
where:
s is the sample standard deviation.
Example
| Col1 | Col2 | Col3 | Col4 | Col5 | Col6 | Col7 | Col8 | Col9 | Col10 | Formula | Description (Result) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 7 | =KURT([Col1], [Col2], [Col3], [Col4], [Col5], [Col6],[Col7],[Col8],[Col9],[Col10]) | Kurtosis of the ata set (-0.1518) |