GAMMADIST
Returns the gamma distribution. You can use this function to study variables that may have a skewed distribution. The gamma distribution is commonly used in queuing analysis.
Syntax
GAMMADIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative)
X is the value at which you want to evaluate the distribution.
Alpha is a parameter to the distribution.
Beta is a parameter to the distribution. If beta = 1, GAMMADIST returns the standard gamma distribution.
Cumulative is a logical value that determines the form of the function. If cumulative is TRUE, GAMMADIST returns the cumulative distribution function; if FALSE, it returns the probability mass function.
Remarks
- If x, alpha, or beta is nonnumeric, GAMMADIST returns the #VALUE! error value.
- If x < 0, GAMMADIST returns the #NUM! error value.
- If alpha ≤ 0 or if beta ≤ 0, GAMMADIST returns the #NUM! error value.
- The equation for the gamma distribution is:
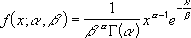
The standard gamma distribution is:
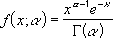
- When alpha = 1, GAMMADIST returns the exponential distribution with:
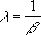
- For a positive integer n, when alpha = n/2, beta = 2, and cumulative = TRUE, GAMMADIST returns (1 - CHIDIST(x)) with n degrees of freedom.
- When alpha is a positive integer, GAMMADIST is also known as the Erlang distribution.
Example
| X | Alpha | Beta | Formula | Description (Result) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 9 | 2 | =GAMMADIST([X],[Alpha],[Beta],FALSE) | Probability gamma distribution of the arguments (0.032639) |
| 10 | 9 | 2 | =GAMMADIST([X],[Alpha],[Beta],TRUE) | Cumulative gamma distribution of the arguments (0.068094) |