About Datasheet view
Datasheet view provides an Excel-like environment for viewing and editing data. It displays the contents of a list or a document library in a grid of rows and columns. Items and columns in the list appear as rows and columns in Datasheet view. You can add and edit rows and columns, apply filters and sort orders, display calculated values and totals, and more.
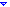
The following illustration shows the Employee list in Datasheet view:
 A row corresponds to a list item.
A row corresponds to a list item.
 A column corresponds to a list field.
A column corresponds to a list field.
 The triangle in the column header is used to filter and sort data.
The triangle in the column header is used to filter and sort data.
 The Total row is used to display aggregate values for each column.
The Total row is used to display aggregate values for each column.
 Software requirements for working with Datasheet view
Software requirements for working with Datasheet view
Your computer must meet a set of software requirements before you can view a list in Datasheet view.
Most list types support the Datasheet view. You can view a list in Datasheet view in two ways:
- By opening a list in a Standard view, and then switching to Datasheet view by clicking the Edit in Datasheet button on the view toolbar
Note If a Standard view does not support Datasheet view, the Edit in Datasheet button will not be shown on the toolbar. For example, the Explorer view of a document library does not support Datasheet view.
- By creating a Datasheet view. Note that you can set the Datasheet view as the default view for a list.
The Datasheet view is independent of all other views of a list. If you add or remove a column from a Standard view, the change does not affect the Datasheet view.
Some list types that do not support the Datasheet view are as follows.
- Discussion board
- Survey
- Image gallery
- Web template library
- Web Part catalog
- Data sources
- Inbox
 Parts of a list in Datasheet view
Parts of a list in Datasheet view
Rows A view contains one or more rows. Each row stores information about an item in the list. For example, a row in the Employee list stores information about an employee.
You can add a row by scrolling to the bottom of the list, and entering data in the star (*) row. You can also edit or delete a row. Your changes are sent to the server after you leave the row and are committed asynchronously. You can continue making changes to different rows, and the view commits your changes in the background. If your changes result in a conflict or error, the view will be updated with information necessary to resolve the conflict or error.
You can change the row height, sort rows based on one or more columns, and hide rows by applying filters.
Columns A view contains one or more columns. Each column stores a particular type of information for all items in the view. For example, the Name column in the Employee list stores the names of the employees.
You can add a column to a list in Datasheet view or Standard view. A column must have a name and must be of a specific data type. You can mark a column as required if you do not want the user to skip the column when entering data. You can also specify additional column settings, such as default value and maximum length. For more information on how to add a column to a list, see Windows SharePoint Services Help. To display Windows SharePoint Services Help, click Help on the page toolbar.
You can modify an existing column or delete a column. You can customize the appearance of a column by showing or hiding columns, rearranging them, adjusting the width, and filtering and sorting rows based on column values. You can also add calculated columns to a list.
Toolbar The toolbar at the top of the view displays buttons for performing common tasks in Datasheet view, such as displaying the task pane or scrolling to the star (*) row. The toolbar is different for different types of lists.
The toolbar is always visible.
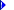
Status bar The status bar at the bottom of the view displays useful information. The following illustration shows a sample status bar:
 The leftmost portion of the status bar displays an icon. When a change you made in the view results in a conflict, the status bar displays the Conflict icon. It displays the Error icon when there are one or more errors in the view.
The leftmost portion of the status bar displays an icon. When a change you made in the view results in a conflict, the status bar displays the Conflict icon. It displays the Error icon when there are one or more errors in the view.
 The text area displays different messages depending on the status of the view. When there are no errors or conflicts, and when the view is not busy communicating with the server, it displays a message on how to display Help on Datasheet view.
The text area displays different messages depending on the status of the view. When there are no errors or conflicts, and when the view is not busy communicating with the server, it displays a message on how to display Help on Datasheet view.
 This area displays information specific to current selection. For example, if the current selection is read-only, it displays "Read-only".
This area displays information specific to current selection. For example, if the current selection is read-only, it displays "Read-only".
 The right-most portion of the status bar displays the communication status indicator. The indicator is on when the view is busy sending data to the server or retrieving data from the server.
The right-most portion of the status bar displays the communication status indicator. The indicator is on when the view is busy sending data to the server or retrieving data from the server.
Task pane The task pane allows easy, context-sensitive access to certain actions, without requiring you to move away from the Datasheet view.
The following illustration shows the task pane for a sample list:
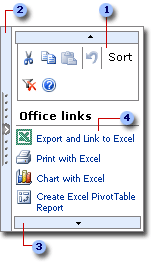
 At the top of the pane is the toolbar. It displays buttons for common commands, such as Cut, Copy, Paste, Sort, and Help.
At the top of the pane is the toolbar. It displays buttons for common commands, such as Cut, Copy, Paste, Sort, and Help.
 Clicking the Net Shade bar hides or displays the task pane. You can drag the bar to resize the pane.
Clicking the Net Shade bar hides or displays the task pane. You can drag the bar to resize the pane.
 Hover over the scroll bar to scroll the pane vertically.
Hover over the scroll bar to scroll the pane vertically.
 The interior of the pane displays various commands.
The interior of the pane displays various commands.