
 | Match Pattern Concepts |
The Match Pattern step is based on a technique called pattern matching. With pattern matching you create a template—or pattern—that represents the object for which you are searching. Then your inspection step searches for the pattern in each acquired image or portion of the image, calculating a score for each match. The score relates how closely the instances of the template match the pattern.
The selection of a good template image plays a critical part in obtaining good results. Because the template image represents the pattern that you want to find, make sure that all the important and unique characteristics of the pattern are well defined in the image. Several factors are critical in creating a template image, as follows:
- Symmetry—A rotationally symmetric template, as shown in Figure 1a, is less sensitive to changes in rotation than one that is rotationally
asymmetric, as shown in Figure 1b. A rotationally symmetric template provides good positioning information but no orientation information.
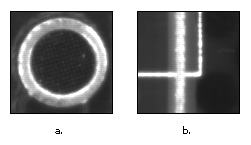
Figure 1 - Feature detail—A template with relatively coarse features is less sensitive to variations in size and rotation than a template with fine features. However, a template must contain enough detail for the software to accurately identify matches to the template. Figure 2a shows a template with good feature detail. Figure 2b shows a template with ambiguous feature detail.
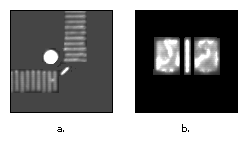
Figure 2 - Positional information—A template with strong edges in both the x and y directions, as shown in Figure 3a, is easier to locate than a template with edges in only one direction, as shown in Figure 3b.
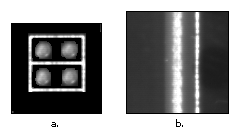
Figure 3 - Background information—Unique background information in a template, as shown in Figure 4b, improves search performance and accuracy.
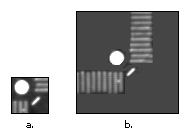
Figure 4
When learning a template, you can choose to mask portions of the template that my vary between images. Masked areas in a template are ignored during the matching process. Masking inconsistent portions of a template can significantly increase the reliability pattern matching.
The following image demonstrates using a pattern matching mask to ignore regions of a template that change from image to image. When the pattern matching algorithm learns the template, it will ignore the serial number and the 2D code that change from image to image.