File/Set File Attributes...
Click or Hover on an item for more ...
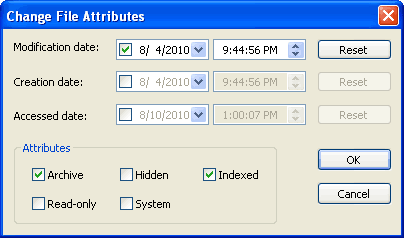
This dialog allows the user to change the file attributes, including system time stamps, of selected files and folders.
Change date manually
You may select each of the three fields (month/day/year, shown here), then type a new value. For example, selecting the day field and typing 23 changes the day to the 23rd of the month shown.
 |
Caution:
The individual fields may not be the same as shown here - they are
determined by the setting for Short date format, found in the Control
Panel / Regional and Language Options applet. You
may open the Control Panel applet here:
|
Calendar tool
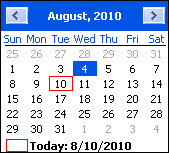 |
The calendar tool allows you to quickly select a date.
You may
|
Change time manually
As with the manual date change, you should select a field, then type a new value. Type "A" or "P" to change to AM or PM.
Attributes
The checkboxes may be checked (set attribute) or cleared (clear attribute) to affect the following attributes:
Archive The archive attribute is used to determine whether a file or folder has been changed. Whenever a file (not folder) is created or saved, the archive attribute is set. Most backup programs may be configured to clear the archive attribute as files are backed up. Read-only This attribute marks a file or folder to prevent overwriting or deletion. Obeying the status of the Read-only attribute is the duty of individual programs using those files; some may ignore any read-only status. In general, the Windows system will warn you before doing deletion or overwriting of Read-only files. Hidden Assigning the hidden attribute flags a file or folder to prevent it from being shown during normal file listings, providing Explorer++ (or Windows Explorer) is not set to view hidden files. Command line operations (eg. Dir) also obey the setting of the hidden attribute. System Windows tries to protect system files (necessary for system operation) in a number of ways, one of which is to assign the system attribute. When this attribute is applied, some operations will respect it and alter their function, ie. refuse deletion. In most cases, this behavior can be over-ridden. Windows can also set the Hidden attribute on a system file, making it superhidden. Indexed Starting with Windows 2000, the indexing service creates indices of files for speed up of searches. With this attribute set, the file is marked for inclusion in the index.
 |
Info: The Date Accessed
(or Accessed date in the dialog) attribute may be considered to be
unreliable as:
The Indexed attribute is not supported by FAT16 and FAT32 file systems. |
