Owning Palette: Conversion VIs
Installed With: Digital Filter Design Toolkit
Scales the coefficients of a filter without changing the characteristics of the filter.
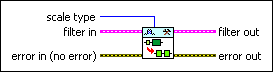
 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
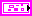
 | scale type specifies the options you use to scale the filter coefficients.
Refer to the Details section of this topic for more information about each scale type.
| ||||||||
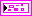
 | filter in specifies the input filter. | ||||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||||
 | filter out returns the scaled filter. | ||||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
DFD Scale Filter Details
This VI calculates the norm values for all impulse responses of the summation outputs in the filter. This VI then chooses an appropriate norm value to use as the reference for scaling the filter coefficients. You can use the following four norm calculation types:
- Time Domain 1-Norm—Specifies that for the impulse response of each summation output, this VI calculates the corresponding norm value by using the following equation:
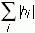
where hi is the impulse response.
This scale type ensures that the dynamic range of the output values is within an appropriate range. However, this scale type also reduces the signal-to-rounding-noise ratio.
- Time Domain 2-Norm—Specifies that for the impulse response of each summation output, this VI calculates the corresponding norm value by using the following equation:
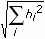
This scale type returns a higher signal-to-rounding-noise ratio than the Time Domain 1-Norm type. However, this scale type cannot guarantee an appropriate dynamic range of the output values.
- Time Domain Inf-Norm—Specifies that for the impulse response of each summation output, this VI calculates the corresponding norm value by using the following equation:
max|hi|
This scale type cannot guarantee an appropriate dynamic range of the output values.
- No Norm—Does not normalize the impulse response.
The four norm calculation types in the list above have decreasing requirements, which correspondingly result in a decreased overflow-handling capability for fixed-point operations such as quantization. Choose the appropriate scale type according to the specific requirements and applications.
Example
Refer to the Scale Filter before Targeting to FXP VI in the labview\examples\Digital Filter Design\Fixed-Point Filters\Single-Rate directory for an example of using the DFD Scale Filter VI.