DFD IIR Notch Peak Design VI
Owning Palette: Special Filter Design VIs
Installed With: Digital Filter Design Toolkit
Designs a notch or peak filter in which the notch or peak is located at the center frequency. You must manually select the polymorphic instance you want to use.
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
DFD IIR Notch Peak Design By Q Factor
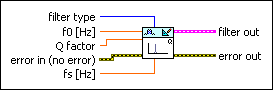
 | filter type specifies the type of filter that this VI creates.
| ||||||
 | f0 specifies the center frequency of the notch or peak. The value of f0 must be greater than 0 but less than half the value of fs. The default is 0.10. | ||||||
 | Q factor specifies the Q factor of the filter, which equals the quotient of center frequency and corresponding bandwidth. The default is 20. The Q factor reflects the relative sharpness of the filter notch or peak. Increasing the Q factor sharpens the notch or peak. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | fs specifies the sampling frequency in hertz. The value must be greater than zero. The default is 1, which is the normalized sampling frequency. | ||||||
 | filter out returns a new filter. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
DFD IIR Notch Peak Design By Bandwidth
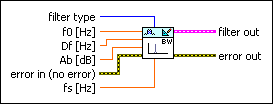
 | filter type specifies the type of filter that this VI creates.
| ||||||
 | f0 specifies the center frequency of the notch or peak. The value of f0 must be greater than or equal to 0 but less than half the value of fs. The default is 0.10. | ||||||
 | Df defines the full bandwidth at the level of –Ab. The default is 0.02.
Df represents 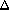 f. f.
| ||||||
 | Ab specifies the attenuation that corresponds to the bandwidth. The default is 3.0103, which corresponds to 3 dB bandwidth, the commonly used bandwidth of a filter. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | fs specifies the sampling frequency in hertz. The value must be greater than zero. The default is 1, which is the normalized sampling frequency. | ||||||
 | filter out returns a new filter. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Examples
Refer to the following VIs for examples of using the DFD IIR Notch Peak Design VI:
- IIR Notch Peak Filter Design VI: labview\examples\Digital Filter Design\Floating-Point Filters\Conventional
- Noise Cancellation for ECG Signal by Notch Filter VI: labview\examples\Digital Filter Design\Floating-Point Filters\Conventional