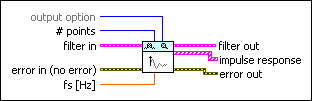
DFD Plot Impulse Response VI
Owning Palette: Filter Analysis VIs
Installed With: Digital Filter Design Toolkit
Plots the impulse response of a filter.
 Place on the block diagram Place on the block diagram |  Find on the Functions palette Find on the Functions palette |
 | output option specifies the impulse response that this VI plots.
| ||||||
 | # points specifies the number of samples that this VI plots for the impulse response. If the value is an integer greater than zero, this VI uses the specified value. If the value is less than or equal to zero, this VI automatically determines the number of samples. The default is –1. | ||||||
 | filter in specifies the input filter. | ||||||
 | error in describes error conditions that occur before this VI or function runs.
The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
| ||||||
 | fs specifies the sampling frequency in hertz. The default is –1, which specifies that this VI uses the sampling frequency of the input filter. | ||||||
 | filter out returns the filter in unchanged. | ||||||
 | impulse response returns the impulse response of the filter. | ||||||
 | error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces.
Right-click the error out front panel indicator and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
DFD Plot Impulse Response Details
Impulse response is the response of the filter to the impulse signal
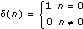
A filter is considered stable if the filter impulse response h(n) approaches 0 as n goes to infinity; otherwise, the filter is unstable.
Example
Refer to the Analyze Impulse and Step Response of Filter VI in the labview\examples\Digital Filter Design\Getting Started\Analyze Filters directory for an example of using the DFD Plot Impulse Response VI.